Protein in the feces of an adult or child is alarm signal, since such a substance in stool Oh healthy person should not be. Its presence often indicates the course of a disease. The only exception may be babies - in such cases, the doctor can draw a similar conclusion based on the fact that the nursing mother eats too much protein-enriched foods.
Analysis of the study of faeces for the presence of such a substance may recommend:
- gastroenterologist.
- pediatrician.
- therapist.
- general practitioner.
However, not in all cases, the presence of protein in the stool indicates the course of any disease.
Cause such a warning sign there may be a large number of predisposing factors, which will differ slightly depending on which age category the person belongs.
Thus, traces of protein in the feces of an adult may appear against the background of a leak:
- inflammatory diseases affecting the intestines;
- infectious processes in the gastrointestinal tract;
- development of malignant or benign neoplasms in the organs digestive system;
- individual intolerance to gluten - a similar disorder is called;
- internal hemorrhages;
- putrefactive dyspepsia;
- pancreatitis and gastritis of any nature;
- hypersecretion of the large intestine.
In children, in addition to the above factors, the detection of protein in stool tests can be provoked by:
- esophagus.
- hyperhidrosis.
- pathological influence, rotavirus or norovirus, which causes the development of infections in the gastrointestinal tract.
- irrational use of some groups medicines especially laxatives.
Often this is due to the fact that parents keep home first aid kit in a conspicuous place or in an area of \u200b\u200bthe living quarters that is easily accessible to the child.
Protein in the stool in infants in the vast majority of cases is found in cases where the mother eats a large amount of protein-enriched ingredients. However, it is worth noting that this is typical for babies who are breastfed.
- dairy and sour-milk products, since they contain cow's milk protein;
- egg whites or yolks;
- soy and corn;
- nuts and beef;
- chicken, turkey and rabbit meat;
- offal and sausages;
- almost all kinds of fish.
In addition, an increase in body mass index can provoke the presence of protein in the feces, which can be attributed to people of any gender and age category.
Indications
Clinicians distinguish a number clinical signs, which are indications for conducting a coprogram to detect protein in the feces. Since such a disorder often causes the occurrence of gastroenterological pathologies, the symptoms will be appropriate.
Thus, among the manifestations are present:
- violation of the act of defecation, which is expressed in or diarrhea, as well as in the alternation of such signs.
- rapid weight loss.
- an increase in temperature, which is accompanied by soreness in the gastrointestinal tract.
- the appearance of pathological impurities in the feces, namely blood and mucus.
- disruption of the intestines.
- attacks of nausea and vomiting - while gagging will not always bring relief to the condition.
- a vivid expression of the characteristic rumbling.
- pain syndrome.
- weakness and fatigue.
In children, such a sign as a developmental delay, both physical and psychological, can serve as an indication - some diseases can affect this.
Calprotectin
Such a soluble protein as calprotectin is the very substance, the presence of which is drawn during the microscopic examination of feces. Only one situation is presented as the norm - calprotectin in children who are not yet one year old.
As for adults, in a healthy person such a substance should be completely absent, nevertheless, gastroenterologists nevertheless formulated an acceptable norm, which is - 0-10mg/ml.
In addition to the above reasons, the appearance of such a protein can increased amount in the body of the following substances:
- zinc;
- magnesium;
- potassium.
However, in the vast majority of cases, its presence is a symptom infectious process, the development of ulcers or tumor-like neoplasms of any nature. If, after conducting a microscopic examination of feces, the doctor found that calprotectin in the feces is increased, then this accurately indicates inflammation of one or another organ of the gastrointestinal tract. In the medical field, the term “fecal inflammation” was derived on this occasion.
Preparation for analysis
In order for the reaction to the protein to be correctly determined in the laboratory, it is necessary to follow the rules for the preparation and collection of feces for the coprogram, which will be similar for both children and adults.
Thus, correct preparation includes:
- before taking the tests, inform the doctor about taking certain medications.
- at the initial visit, inform the clinician about traveling to other countries - this is necessary, because infection of the gastrointestinal tract with certain viruses, bacteria, or protozoa is typical for individual regions.
- a ban on the use of feces that have already been in contact with water or urine, detergents or other chemicals.
In addition, the procedure is postponed if the patient is menstruating or a bleeding hemorrhoid is diagnosed.
- implementation of hygienic treatment of the anus and genitals.
- collection of feces with a special spoon in a sterile container - such devices are issued by the attending physician or purchased at a pharmacy. For such a study about a teaspoon of feces is needed.
- tightly closing the container and making a signature indicating the time of collection and personal data of the patient.
- after that, provide everything you need to the gastroenterologist. If it is not possible to do this immediately, then it is allowed to store the copro-material in the refrigerator, but not more than eight hours.
Decryption
Get to the doctor in about five working days. At this time, a large or little patient additional laboratory and instrumental examinations may be prescribed.
During decoding, the following norm indicators are taken into account, depending on the age category:
- infants from one to six months - 538 mcg / g.
- babies from six months to three years of age - no more than 214 mcg / g.
- children from three to four years old - up to 75 mcg / g.
- from four years - no more than 50 mcg / g. The same rule applies to adults.
If indicators were found higher than those described, then this indicates a positive reaction to the protein in the coprogram.
Since the presence of protein in the feces indicates the presence of a particular pathology, patients may be diagnosed with one of the following disorders:
- gastritis or oncology of the stomach;
- ulcerative lesions of the duodenum or stomach;
- proctitis or anal fissure;
- duodenitis or enteritis;
- or ;
- ulcerative, fermentative or putrefactive form.
Depending on the identified pathology, treatment can be directed to:
- taking medications, in particular enzyme substances.
- adherence to a healthy diet.
- implementation of physiotherapy procedures.
- course completion therapeutic massage or LFC.
- surgical intervention.
It should be noted that often therapy is complex. If a positive reaction to protein is established in the baby, then drug treatment be reduced to a minimum.
Prevention
From all of the above, it follows that protein in the feces does not always mean the presence of pathology, however, there are several rules that will help prevent the appearance of such a symptom. They should include:
- control over what a breastfeeding mother eats during breastfeeding It is best to minimize the intake of protein foods. This can be done only with the permission of the pediatrician;
- storage of medicines in hard-to-reach places for children;
- taking medications strictly according to the doctor's prescription and in compliance with the daily dosage;
- maintaining normal body weight for both adults and children;
- regular visits to children's specialists;
- passing at least twice a year examination by a gastroenterologist - for adults.
By itself, the protein in the feces is not a disease, which is why it cannot harm a person's life. However, its presence indicates the possible presence of any gastroenterological pathology, each of which has its own complications, which, among other things, can be fatal.
INTERPRETATION OF THE ANALYSIS OF feces
(Study physical properties feces)
The number of daily bowel movements varies considerably and depends on the condition gastrointestinal tract, quantity and composition of food as well as the financial well-being of the patient. With a plant-based diet, the amount of feces is much greater than with the use of food of animal origin.
An increase in the daily amount of feces (polyfecal matter) up to 1.5-2 kg / day. may be due to:
secretory insufficiency - a violation of the secretion of digestive enzymes: the stomach, duodenum, pancreas, small and jejunum;
syndrome of insufficient absorption (malabsorbtion syndrome);
Intestinal infections, poisoning.
According to the consistency, dense, or shaped, densely or liquid-mushy and watery feces are distinguished. The shape is normally cylindrical (sausage-shaped), with stenosis of the colon - "pencil shape". With spastic colitis, constipation - " sheep feces". Liquid watery stools occur with accelerated peristalsis (provided there is enough water in the body).
The normal brown color of feces is due to bilirubin derivatives - stercobilin and mesobili-fuscin. The color is also affected by the nature and composition of the food, the medications taken, the intake or absence of bile, the presence of blood (in case of bleeding).
Here are some of the causes of color change.
Red. Eating beets, grapes (red variety), bleeding from the colon, hemorrhoids.
Black. With bleeding from the stomach and duodenum. Blackening occurs due to the oxidation of iron from red blood cells. The black color of feces is also characteristic when taking iron, bismuth preparations, activated carbon, blueberry, black currant, coffee.
Green. At elevated content bile in a purely vegetable diet. Orange yellow. Dairy diet.
white gray. With the cessation of the flow of bile into the intestines.
The smell is due to the presence of skatole, indole, phenol, ortho- and paracresols in the excrement. These organic compounds of the aromatic series are formed during the breakdown of proteins. They have a very persistent peculiar, specifically unique aromatic bouquet, which is enhanced by the decay of proteins.
Study of the chemical properties of feces
In the chemical study of feces, pay attention to the following points.
Blood
Normally, feces give negative reactions to "hidden" blood. We are talking about those conditions when the bleeding is very small. Own erythrocytes are successfully digested in the intestines to blood pigments that have peroxidase properties.
Minor bleeding can occur, for example, with gastric and duodenal ulcers, when the situation is under control and the ulcer can be “healed” with pills. Otherwise, massive bleeding occurs, in some cases - suddenly.
A malignant tumor may “leak”; this usually occurs at a stage where surgery can save the cancer patient. That is why the detection of blood in the feces is very important diagnostically. At the same time, do not forget that bleeding from the nose and gums also gives a positive reaction to "hidden" blood.
Feces for occult blood are given after a three-day diet, in which meat, fish, eggs, and green vegetables are excluded from the diet.
The bile pigment stercobilin in the feces is a mandatory norm. It is thanks to this component that the chair acquires Brown color. If there is a lack of it, the feces become discolored.
Origin and functions of stercobilin
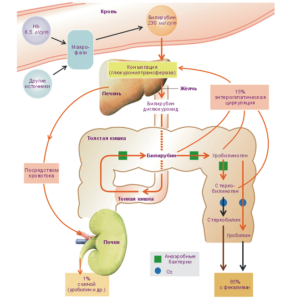
With the destruction of hemoglobin, the pigment bilirubin is formed, which is processed in the intestine with the help of bacteria into stercobilinogen. The resulting substance is absorbed by the walls of the intestine, penetrates into the blood, and then into the liver and kidneys. After that, stercobilinogen in the process of oxidation is converted into stercobilin.
This coloring pigment gives the stool its typical brown or brown tint. It is noteworthy that stercobilinogen is colorless. After getting through the blood vessels to the kidneys, stercobilin is transformed into urobilin. Once it reaches the kidneys, it is excreted in the urine. The main part of the transformed stercobilinogen is found in feces (95% of this pigment), the remaining 5% is in urine. All these substances, which are normal degradation products (urobilinogens), are formed at a constant rate.
The color of feces depends on the bile pigment. However, oxidized stercobilinogen performs not only the function of staining feces.
It is the presence of this substance that shows how properly the liver, spleen work and metabolism occurs.
By determining the amount of stercobilin, specialists manage to recognize the signs of suprahepatic jaundice in time. This pigment helps to assess the available volume of red blood cells and hemoglobin. This is possible because it is in the liver that bilirubin is formed as a result of the breakdown of red blood cells and the release of hemoglobin.
Normally, the content of stercobilin in feces should reach 75-350 mg per day. A decrease or increase in this indicator is a signal that serious malfunctions are occurring in the body. The reaction to the stercobilin pigment was negative in childhood considered the norm. Important biological role stercobilin lies in its ability to be a kind of marker of the state of health.
When does stercobilin appear?
 A newborn child initially has imperfectly functioning internal systems. The gastrointestinal tract of infants has yet to adapt to the conditions of life outside the mother's womb. Therefore, stercobilin appears as soon as it is formed in the intestine normal microflora. And this happens often at the age of 5 - 6 months. It was at this time that a positive reaction to the coloring pigment was first detected. But a newborn and a child under 5 months of age does not have this substance in the feces, which is considered normal.
A newborn child initially has imperfectly functioning internal systems. The gastrointestinal tract of infants has yet to adapt to the conditions of life outside the mother's womb. Therefore, stercobilin appears as soon as it is formed in the intestine normal microflora. And this happens often at the age of 5 - 6 months. It was at this time that a positive reaction to the coloring pigment was first detected. But a newborn and a child under 5 months of age does not have this substance in the feces, which is considered normal.
Stercobilin and bilirubin are distributed according to this principle:
- Bilirubin is excreted in the feces of newborns and children who eat breast milk. It is he who gives the feces a green color.
- In the feces of a baby 5 - 8 months old breastfeeding And artificial feeding both substances are present.
- In children older than 8 months, only stercobilin is found. In the future, bilirubin in the stool is no longer present, which is the norm.
As the bile pigment in the stool grows, the child completely replaces the bilirubin. In the coprogram of children, starting from 6 months, the bile pigment is denoted by the word "present". Over time, a positive indicator will have to reach 75 - 350 mg. Absence given substance causes acholic stool. Allocations acquire a clayey colorless consistency, which indicates a complete blockage of the biliary tract. In any case, so that this situation does not mean, it is important to contact a specialist in time. Only he can figure out what it means.
How is stercobilin detected?
The study of stercobilin in feces and the functionality of the organs of the gastrointestinal system occurs through the implementation of a number of laboratory research. Among the effective and demonstration methods refers to the coprogram. This analysis of feces is also important for setting accurate diagnosis, and to control the prescribed course of therapy. It provides the following information:
Oxidized stercobilinogen in feces can be determined by several methods. Qualitative stool analysis involves the use of mercury dichloride, which interacts with bile pigment. The reaction is expressed in the formation of a pink substance of varying intensity. Carrying out this technique takes a day - during this time the necessary reaction must pass. However, the absence of stercobilin will cause the resulting substance to have a green color.
The determination of stercobilin can also take place by using a quantitative method. This method is used infrequently, mainly when the color of the stool is not sufficiently intense. It is based on a change in the color of feces as a result of a reaction with paradimethylaminobenzaldehyde. This reagent, when interacting with stercobelin, stains the feces in a bright red color. It is noteworthy that the more intense the color, the more bile pigment. It is possible to draw conclusions by using a quantitative method using spectrophotometry.
Preparation for the study of feces
Fecal analysis will be as informative as possible if you properly prepare for its delivery. Normally, adults and children should begin preparation a few days before visiting the laboratory. Its essence lies in cleansing the intestines in order to ensure the absence of food residues, plant and muscle fibers in the feces. To do this, it is recommended to follow for 2 - 3 days special diet: either according to Pevzner or according to Schmidt.

The Pevzner diet involves the inclusion in the diet of white and black varieties of bread, meat, sauerkraut, buckwheat, rice, potatoes, apples and butter. Both in an adult and in a child, the daily menu should be high-calorie.
The Schmidt diet is considered more sparing, according to which you need to eat 5 times a day. The main ones are dairy products, butter, eggs, meat, potatoes, oatmeal.
If, for health reasons, or due to an urgent test, it is not possible to follow a diet, it is recommended that you stop drinking coffee, tea and alcohol at least a day in advance.
Laxatives, antidiarrheal drugs, suppositories, as well as medicines based on barium sulfate, bismuth can affect the consistency, color and composition of the stool. Therefore, you need to stop using them before passing the analysis.
Norm indicators
The presence of salts is considered normal. fatty acids in a small amount. There is a strictly limited amount of normal iodophilic intestinal microflora. At the same time, starch must be absent.
The norm is a negative reaction to bilirubin, occult blood. a negative protein is also considered normal. In children infancy determination of bilirubin in feces is acceptable. The breakdown product of bilirubin must be determined without fail in the feces of an adult. Negative reaction on the pigment stercobilin is a signal pathological processes in organism. A change in its quantity always occurs in certain diseases.
Causes of changes in the composition of feces
Being a marker of the state of health, stercobilin is able to give a signal of emerging malfunctions in the digestive system. Its amount may increase or decrease depending on what kind of pathological processes have arisen.
An increase in coloring pigment usually occurs when red blood cells rapidly decay. The reason for this may be hemolytic anemia(jaundice). At hemolytic jaundice staining is observed skin in intensive yellow. High level bile pigment is observed during hemolysis of erythrocytes due to poisoning with poisons, medicines. The cause of increased stercobilin is also the excessive work of the spleen.
If the stercobilinogen oxidation product is not detected in the feces, it can be confidently stated that bile duct completely clogged. Usually this condition occurs due to its compression by a stone or tumor. At the same time, it produces light feces, and the skin turns yellow-green.
The reaction to stercobilin is negative when:
- stones in the biliary tract;
- tumors of the head of the pancreas;
- growth of lymph nodes;
- lymphadenomopathies;
- acute hepatitis, pancreatitis, cholangitis.
If the reaction to bilirubin is positive, then there is a dysbacteriosis in the body, complicated antibiotic therapy. This also happens with severe diarrhea.
White blood cells in the feces are considered abnormal. Their presence indicates a possible colitis, enteritis, intestinal tuberculosis, ulcerative colitis, helminthic invasion.
When conducting research, they also take into account the fact that urobilin in the urine can significantly decrease due to the use of antibiotics. a wide range actions. Often the amount of this substance increases in the feces in parallel with a decrease in the urine.
Characteristics of the detrital mass
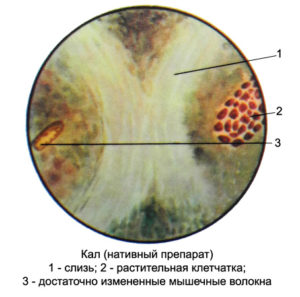
What is detritus? It is small needle-like elements of digested food, processed bacterial cells, particles of the epithelium of the gastrointestinal tract (tissue detritus plus intestinal epithelium) are natural waste products. At microscopic examination granular amorphous formations can be seen. Chyme in the stomach or intestinal chyme is a semi-liquid substance in the form of a slurry of digested food, gastric and intestinal juice, secretions of glands, and bile. Under the influence of enzymes, all this turns into feces in the process of complex gastric and small intestine digestion.
Leaving the stomach, chyme enters duodenum, after - in colon where moisture is extracted from it. At proper nutrition in a soft stool, a large amount of detrital mass is observed, as in a solid mass (with a predominance of vegetable fibers), and liquid fecal stools contain small amounts of detritus.
But what are the acceptable norms for the index of these particles? And how is scatology or stool examination performed in a baby or an adult?
Basic research methods
Coprogram or general analysis feces are carried out by a laboratory assistant medical institution. If detritus is found in the coprogram, its amount is estimated, as well as the following parameters:
- volume, consistency, color, and odor of the fecal sample;
- acidity index;
- presence of mucus spotting, soluble protein, leukocytes;
- indicators of stercobilin, bilirubin, ammonia;
- the amount of fatty acids, soap, as well as neutral fats.
No less important are such contained substances as muscle fibers, connective tissue, starch in feces and vegetable fiber. The deviation of the received data from the norm also indicates the presence of problems. Each indicator should be assessed in relation to the age category. For children of the chest group, babies on artificial feeding, older children, adolescents and adults, there are their own indicators of the norm. The presence of deviations and their causes will indicate the problem, a specific disease. Thus, the analysis is deciphered. Also, do not forget about the nutritional habits of each person, the lifestyle that determines the plant and animal (organogenic) fecal composition.
Conducting an analysis
The process of studying the composition of feces is carried out under a microscope. Its small fragment is placed between two glasses and a study is carried out on the amount of waste products. If the stool is too hard, it is diluted with water in a centrifuge, and in this case only the part that entered the liquid is considered detritus. Its quantity is determined by the "+" sign from one to five. The doctor can postpone the delivery of such an analysis only if the patient:
- is taking any medication;
- examination of the gastrointestinal tract.
In this case, the results of the analyzes may be distorted and affect correct setting diagnosis.
Detritus in the feces of a child. Preparation for analysis
Before conducting a stool test in a child, it is necessary to stop giving him medicines (if he takes them) a day or two before. Since their reception may affect the results of the test. Even if he is constipated, he should not be given laxatives or enemas. For infants it is very important not to take before this analysis nutrient mixtures, but only mother's milk, as they can also affect the data obtained. All indicators are evaluated in a complex, only such a study will show a complete picture of the existing problem.
If particles of detritus are found in the feces of the baby, do not panic. This phenomenon does not signal a disease, but is the norm. The composition of the detritus mass includes what the baby eats. But at the same time, the mass particles should be small, almost homogeneous.
Detritus rate and pathology indicator
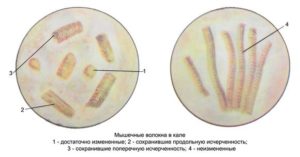
 The stool contains both columnar epithelium and squamous epithelium. The squamous necrotic epithelium in the feces of an adult is strong enough and does not have of great importance when diagnosing. Cellular detritus (dying epithelial cells of a cylindrical shape) can come from any part of the intestine during tissue exfoliation (necrosis). But if such necrotic detritus is found in mucous secretions in combination with high content leukocytes and erythrocytes, it can be assumed that there is an inflammatory process in the intestine.
The stool contains both columnar epithelium and squamous epithelium. The squamous necrotic epithelium in the feces of an adult is strong enough and does not have of great importance when diagnosing. Cellular detritus (dying epithelial cells of a cylindrical shape) can come from any part of the intestine during tissue exfoliation (necrosis). But if such necrotic detritus is found in mucous secretions in combination with high content leukocytes and erythrocytes, it can be assumed that there is an inflammatory process in the intestine.
In a healthy person - plant and animal food completely recycled. When emptying the intestines in the stool, detrital particles will be in an amount that does not exceed the norm. In other cases, deviations can be caused by the following reasons:
- the presence of gastritis with high or low acidity;
- peptic ulcer;
- lack of gastric juice;
- growth pathogenic flora in the intestines;
- weak immune system;
- rejection by the body of certain types of products;
- the presence of an infection;
- too rapid evacuation of feces from the large intestine.
Treatment Methods
The method of treatment of diseases associated with pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract and deviations from the norm of indicators of detritus particles involves, first of all, a change in lifestyle, a variety of diets. It must contain plant foods.
It is equally important to adhere to therapeutic diet prescribed by a doctor after diagnosis specific disease gastrointestinal tract. Don't forget also about physical activity, since many digestive diseases are associated precisely with physical inactivity. Medical or physiotherapeutic treatment of the disease is prescribed by a doctor.
Considering that currently the biggest problem modern man are violations of the intestinal microflora, therapy is carried out by the most gentle methods aimed at restoring correct operation GIT.
Fecal stool, like urine, is the end product of human life. They are formed in the large intestine as a result of various biochemical processes. They include water, undigested food particles, metabolic products, bacteria and more.
Pevsner's diet. Its main goal is to load the human body as much as possible. Within one day you need to eat 400 g of white bread, 250 g fried meat, 100 g butter, 40 g sugar, buckwheat or rice porridge, fried potatoes, lettuce, sauerkraut, compote and apples. The calorie content is quite high - 3250 kcal. If you choose this diet, then be sure to consider the state of your digestive system. It will detect even a small degree of indigestion;

The Schmidt Diet. This daily diet includes 1-1.5 liters of milk, 2-3 boiled eggs, White bread And butter, 125 g minced meat, 200 g mashed potatoes, 40 g boiled oatmeal. Daily calorie content- 2250 kcal. Food should be divided into 5 receptions.
Preparing for a stool test for occult blood
Before examining the stool for occult blood, doctors strongly recommend that patients eat the following foods: green vegetables (cucumber, cabbage, zucchini, green peppers, broccoli and others), meat products, fish, eggs.
In addition, you need to refrain from taking medications that contain iron.
In the case when a person needs to urgently make a coprogram and identify what the reaction to stercobilin in the feces will be, or the patient cannot adhere to one of the above diets for health reasons, experts recommend not to use alcoholic drinks and coffee.
General rules for assembling a chair
For research, you need to take only morning feces. After a bowel movement, the patient collects a small amount of feces with a wooden spoon or spatula and places it in a clean container, then closes it tightly. In order to detect stercobilin in the feces, 10-15 g of stool is enough.

1. Rinse well before collecting faeces back region body.
2. Women should not collect feces during menstruation, because the stool should not contain menstrual blood.
4. You can not collect feces after the introduction of candles and other drugs that affect the color of feces.
After collecting faeces, wash your hands thoroughly with soap and dry them with a clean towel!
To detect fecal helminth eggs, feces must be fresh and stored in a warm place until delivery to the hospital.
For bacteriological examination of feces (especially for stercobilin in the feces of a child), the patient needs to obtain a sterile cotton swab. Insert handset into anus there will only be a specialist.
To discover hidden blood in feces, it is necessary to exclude meat and mushrooms from the diet for 3 days before analysis, as well as medicines with iodine, bromine and iron. On the fourth day, the patient collects the faeces and sends them to the laboratory.
In severe constipation, a special colon massage should be performed. If this does not lead to anything, doctors do an enema and take only a dense stool for examination.
Normal indicators of the analysis. Stercobilin in feces is positive - what is it?
Tests for occult blood, protein, bilirubin should usually be negative. If you have normal analysis feces, the reaction to stercobilin is positive, since it is this pigment that gives the feces a brown color.
Indicators in case of deviation from the norm
The main indicators that are uncharacteristic of a normal stool:
1. Shapeless feces.
2. Too hard feces.
3. Pungent smell.
4. The presence of visible or hidden particles of blood.
5. positive reaction for bilirubin.
6. The presence of muscle fibers.
7. Found fat in the stool.
8. Change in color (black or white clay), which indicates that there is no stercobilin in the feces.
9. The presence of food particles.
10. The presence of leukocytes (white blood cells).
12. Giardia and amoeba.
Analysis of the results of a coprogram in a child
The interpretation of the analysis of the feces of children should be carried out by a pediatrician or pediatric gastroenterologist. In the study, it is important to take into account the age of the child and the nature of the food. In infants under one year of age who are not yet taking solid food, allowed high concentration in the feces of undigested muscle fibers and fats.

If the baby has a deficiency of lactase (an enzyme that breaks down milk sugar- lactose), starch can be found in the feces.
With dysbacteriosis, stool analysis is additional method research. Microbiological analysis is considered to be the main one. However, the coprogram shows the stercobilin in the feces is positive or negative in the child, whether the intestines are inflamed (mucus and fecal leukocytes are found in the feces), whether the process of digestion and absorption of carbohydrates, proteins and fats is disturbed (muscle fibers, fats, starch are found in the stool). After the analysis, the doctor can conclude that the child has a dysbacteriosis.
If the baby has hepatitis, the feces become grayish-white in color and resemble clay. This suggests that there is no stercobilin in the feces of the baby (which turns normal stool brown) and bile stops flowing into the intestines.
If a child has chronic pancreatitis, the frequency of his bowel movements per day will be increased, the color of the stool will turn gray. The consistency of feces in pancreatitis is pasty, the smell is sour. Fats, starch and a large number of leukocytes can also be detected - all these are signs of inflammation in the body and that there is no stercobilin in the feces.
The child and the presence of latent blood in it is a consequence of the formation of ulcers in the stomach.
Diseases that provoke changes in the composition of feces in adults
In diseases of the digestive system, it is very important to monitor the increase in the amount of feces during the day. This usually occurs due to pathological processes leading to impaired digestion and absorption of food and water in the intestine. A decrease in the amount of stool per day is observed in diseases that are characterized by prolonged constipation, such as peptic ulcer. Let us consider in more detail the main changes in the composition of feces, which indicate the appearance of various diseases:
1. Discoloration of feces is observed, as a rule, with cholestasis. At the same time, they form gallstones that interfere with the flow of bile into the intestines. Jaundice develops, the stool loses color, acquiring a white tint. In the case (we are talking about a study when stercobilin is determined in the feces) of a positive reaction, the color of the feces would be brown, and the state of the body would be normal. The appearance of discolored feces is mainly combined with nausea, belching, fever. If the feces turn black, this means that the patient has a stomach ulcer. It's related to the break blood vessels at the bottom of the ulcer. Esophageal varices are common in people with cirrhosis of the liver.

2. Appearance of blood particles in the feces. If fresh blood was found during visual examinations, then this indicates the appearance of diseases such as ulcerative colitis, haemorrhoids, anal fissures, dysentery.
3. Change in stool odor. Sharp, sour bad smell feces are the result of the appearance inflammatory processes in the body, a sign of chronic pancreatitis and confirmation that stercobilin is absent in the feces. This disease is characterized by insufficient production of pancreatic juice, which is involved in the process of digestion of carbohydrates, proteins and fats in the body. A large number of undigested residues food leads to an increase putrefactive bacteria, which give rise to pungent odor feces.
4. The presence of protein in the stool indicates the occurrence of chronic atrophic gastritis, in which the stomach does not produce gastric juice. With its lack of protein in small intestine does not break down, but leaves the body with feces. Other symptoms of chronic atrophic gastritis are heaviness in the stomach after eating, belching with rotten smell. Chronic pancreatitis also leads to the appearance of protein in the stool. Its symptoms are bloating, unpleasant pain in the epigastric region or around the navel, low index body weight.
6. Positive reaction to bilirubin. Bilirubin is a bile pigment, which, under the influence of the microflora of the large intestine, is converted into stercobilin. And food poisoning lead to an increase in the rate of passage of food through digestive tract. The bile bilirubin simply does not have enough time to turn into stercobilin in the colon, and then it is simply excreted into the feces. A positive reaction to stercobilin in feces ( positive result is the norm) would mean that everything in the body is in order.
7. The presence of mucus in the stool. Mucus is a jelly-like substance that serves to better glide food. It is impossible to detect with the naked eye, because it is evenly mixed with feces. The appearance of mucus in the feces indicates inflammation of the colon, as well as the occurrence infectious diseases: dysentery and salmonellosis.
8. The appearance of muscle fibers in the stool is a consequence of chronic atrophic gastritis and chronic pancreatitis.
9. The presence of fat in the stool is the result of a violation of the activity of the pancreas, which produces a special substance - lipase, which breaks down fat in the intestines.
10. The detection of fecal starch is characteristic of chronic pancreatitis.
11. The presence of leukocytes in the stool. Leukocytes, or white blood cells, are designed to fight infections in the body. If they appear in the feces, then this indicates the occurrence of inflammatory processes in the intestines.

So, now we know that the work of the digestive system can be judged on the basis of an analysis called a coprogram. Doctors strongly recommend doing it every 6 months to track the appearance possible diseases in organism.