There are about a million microorganisms in the human oral cavity various types and strains that easily get along with each other and do not cause discomfort to the owner if his immune status is normal.
When immunity decreases, opportunistic microorganisms begin to actively multiply and, more often, stomatitis of fungal etiology begins.
Most often, four fungi of the genus Candida suppress the vital activity of other microorganisms: albikans, glabrata, parapsilopis and tropikalis. However, more often the first one wins - albikans Candida, which causes baking on the mucous membrane and cheesy deposits. When you try to get rid of plaque with physical effort, pinpoint bleeding appears.
Candida fungi are activated when immunity decreases, no matter what causes it. Their active reproduction suppresses the vital activity of other microorganisms, acid-base balance V oral cavity is violated - the environment becomes acidic.
The disease most often affects children early age– their immunity has not yet been formed and their diet is monotonous, but it can develop in adults.
Is it possible to treat oral fungus at home? folk remedies or without medical supplies impossible to get by?
Symptoms of oral candidiasis
Symptoms of candidiasis depend on the stage of development of the disease and general condition sick. Infants and elderly adults are most often affected - about 90% of cases.
- Initial stage of the disease
Symptoms of the disease on initial stage: after fungi of the genus Candida begin to actively multiply in the oral cavity, sensations of dryness and burning appear. The mucous membrane turns red, swells, and blood vessels are clearly visible on it. All this happens because toxins from the activity of the fungus dissolve the surrounding tissue.
- Progressive disease
The fungus then forms pseudomycelium (mycelium). It looks like a cheesy coating that rises above the surrounding mucosa. The affected area expands, the plaque becomes denser - it already includes food debris, destroyed and exfoliated epithelium, fibrin, keratin, particles of bacteria and other fungi. The affected areas merge with each other, they are already localized not only on inside cheeks, but also on the gums, on the tongue, in the sublingual space, on lymphoid tissue tonsils and lips.
While the plaque is in the form of individual dots, it is easily removed, exposing the bright red mucous membrane, sometimes with pinpoint bleeding, as from needle pricks. In the future, if the deep layers of the mucous lining the oral cavity are damaged, it is almost impossible to remove the plaque.
Another sign of thrush - as candidiasis is more often called - is mycotic seizure. Microcracks appear in the corner of the mouth, covered with transparent scales or a whitish cheesy coating. Drooling increases; in young children - they do not yet know how to swallow reflexively - drool drips onto the chin, and the skin of the face and neck becomes irritated. Rashes appear on delicate skin, which also cause pain.
If left untreated, the symptoms of candidiasis increase: discomfort in the mouth becomes constant, pain occurs when swallowing, and eating becomes difficult. When fungal flora spreads to the tonsils, it becomes painful to swallow.
Children often have a fever - the active activity of microflora causes intoxication of the body. In adults, a rise in temperature is rarely observed.
Oral fungus causes the following complications: allergization of the body and depletion of defenses, that is, decreased immunity. Children begin to lose weight, vital activity decreases, and developmental delays appear - both physical and mental. It is impossible to feed a sick child; he develops anemia and vitamin deficiency. Treatment should begin when the first symptoms of the disease appear.
Causes of oral mycosis
In adults, factors influencing decreased immunity and increased activity of opportunistic flora may be the following:
In children, thrush is most often caused by dysbacteriosis and violation of hygiene rules.
Thrush is not « internal disease» . When unstable immune status it can be contracted through kissing, sharing utensils or a toothbrush, or through food - if you eat "from one piece". If the mother has candidiasis, the newborn can become infected while passing through the birth canal. Children also often become infected from animals.
Treatment of fungus in the mouth
Treatment should begin with dietary adjustments. Sour, salty, and foods containing yeast should be excluded from the diet. Also, you should not eat too hot or cold food - this increases the pain.
Prescribed drugs that destroy the fungus - "Nystatin", "Levorin", "Fluconazole", "Diflucan", "Clotrimazole", "Miconazole". The dosage of the drug and the frequency of administration depend on the patient’s age and clinical picture - you must follow all the recommendations given by the doctor.
The oral mucosa is treated with ointments and creams: "Clotrimazole" or nystatin solution "Lugol".
Adults rinse their mouths - especially after meals; children use gauze swabs to treat the oral cavity with solutions:
- boric acid – 2%;
- iodinol;
- Boers – 2%.
 In treatment, it is important to avoid self-prescription, especially when it comes to children.
In treatment, it is important to avoid self-prescription, especially when it comes to children.
Aniline dyes are used to treat children - most often methylene blue, sometimes brilliant green. Currently, drugs are produced that contain lidocaine - they are recommended to be used before meals. Additional treatment for adults - lozenges that are used for sore throat or pharyngitis: "Lisobakt", "Lizak" and the like.
Assign antihistamines, eliminating swelling and itching in the oral cavity, complement the treatment "Calcium gluconate" and immunomodulators. The therapeutic regimen is supplemented with iron supplements - "Conferon" or "Ferroplex".
When treating children, they try to use folk recipes- treat mucous membranes soda solution babies and sea buckthorn oil And carrot juice those who are older. A decoction is also used oak bark, cranberry juice, chamomile and calendula decoction. These measures will help to temporarily stop the course of the disease, but as soon as “dirt” gets into the oral cavity or the baby’s diet changes, candidiasis will reappear. To avoid the disease becoming chronic, antimycotic drugs must be used for treatment.
Thrush therapy is enough difficult process, should not be taken lightly. IN severe cases at the onset of atrophic processes, injectable medications can be used - “Amphotericin B” intravenously.
The course of treatment for candidiasis is at least a week. “One pill and everything will go away”- This is just a publicity stunt.
Prevention of fungal diseases in the mouth
To prevent the exacerbation of thrush, it is necessary to treat all diseases of the oral cavity in a timely manner, properly care for dentures, and observe hygiene measures - brush your teeth regularly.
In case of mucous membrane injuries, it is necessary to treat them disinfectant solutions using rinses.
You can’t use someone else’s dishes, much less "to borrow" toothbrush. Adults should – if possible – stop smoking.
Children in the first year of life are treated by a pediatrician; candidiasis in older children is treated by dentists.
Most people have fungi of the genus Candida in their mouths, which do not manifest themselves at all until a certain time. But if protective properties the body for some reason begins to decline, this leads to their development. Fungi affect not only internal cavity mouth, but also the corners of the lips. In this case, you should not self-medicate, as this can lead to serious complications.
Causes
Fungus (thrush or candidiasis) appears when conditions are favorable for them. These include:
- decreased immunity;
- violation hormonal levels;
- general deterioration of the body;
- imbalance of microflora;
- radiation therapy used for cancer;
- malocclusion or damage to teeth causing injury to the oral mucosa;
- wearing dentures;
- violation of hygiene rules.
Very often, fungus in the mouth affects young children under one year old or older people. Women are much more susceptible to the occurrence of this disease. You can become infected with candidiasis through contact and everyday life or when using general subjects: dishes, toothbrush, towels, etc. Newborn children become infected from their mothers, and smoking people They get this infection from smoking one cigarette.
Main symptoms
As soon as the fungi penetrate the cells of healthy tissues, they begin their active reproduction, while secreting enzymes and forming loosely bound cellular compounds - pseudomycelia. This leads to irritation of the mucous membrane and destruction of adjacent tissues.

Thus, if a fungus occurs in the mouth, its symptoms may manifest itself as follows:
- dry mouth;
- increased sensitivity;
- redness;
- edema.
As fungi begin to multiply, rashes appear in the mouth white. At first, they resemble curdled grains, after which a coating appears in the form of a milky film. She covers separate areas, which, as they increase, begin to merge. Such areas covered with white plaque are called plaques. They can appear on the cheeks, gums, tonsils, and palate. If this infection affects the lips, then their surface is covered with white scales and flakes.
At the very beginning of the development of the disease, plaque is removed quite easily. The surface freed from it begins to turn red and becomes covered with small ulcers. This happens due to the fact that fungi secrete special enzymes that destroy cells of nearby tissues. After some time, the tissues begin to be affected more and more deeply.
At this stage, fungus in the mouth is characterized by the following symptoms:
- itching and burning;
- irritating effect of hot, spicy, hot foods;
- temperature increase;
- difficulty swallowing;
- the occurrence of mycotic seizures;
- difficult passage of food.
Diagnostics
If a fungus appears in the mouth of an adult, you should seek medical attention. qualified assistance see a dentist or periodontist. If the fungal infection has spread beyond the oral mucosa, you will need to consult an infectious disease specialist or mycologist.
First, the doctor examines the patient and asks him about the characteristics of the disease. To clarify clinical picture candidiasis, carried out the following types tests:
- scraping from affected areas of the oral cavity;
- general analysis blood;
- determination of blood sugar levels.
If such a need arises, the doctor may order additional tests to clarify individual characteristics organism and the nature of the course of this disease. Each patient has his own treatment regimen.
Treatment
If a fungus occurs in the mouth, it is treated using general and local action which should only be prescribed by a doctor.
Local treatment consists of using preparations for rinsing, treating the oral cavity, applications, etc. These can be disinfectant and alkaline solutions and agents that help restore damaged mucous membranes and provide bactericidal effect on the inner surface of the oral cavity.
Diet
To successfully cure fungus in the mouth, you must follow a diet and correct mode nutrition. The diet should not contain hot, salty, hard, sour and spicy foods and dishes that cause irritation to the oral mucosa. It should also be abandoned sweet food, capable of activating the growth of fungi.
You need to eat small portions several times a day. Products must be warm, soft, contain a large number of vitamins The specific menu should be drawn up by the attending physician.
Prevention
To prevent fungus in the mouth from manifesting itself in all its glory, preventive measures should be taken, including:
- careful hygiene;
- proper nutrition;
- care for gums and teeth;
- rejection of bad habits;
- strengthening the immune system;
- timely treatment of chronic diseases;
- systematic visits to the dentist.

In addition, you need to use only your own, wash dishes thoroughly, disinfect towels from time to time, and try not to contact sick people.
Fungus in a child's mouth
Children may be born in the maternity hospital if they are touched by medical staff who are carriers of candidiasis. On the skin of infants, fungi remain active for 2 hours. Parents can also infect their baby through kissing.
After a year, infection occurs when the child begins to put toys into his mouth, especially strangers. Originated in preschool age candidiasis occurs due to weak immunity or long-term use of antibiotics.
This disease is also treated with traditional medicine.
Conclusion
Thus, if fungus occurs in the mouth in adults and children, you should consult a doctor who will prescribe competent treatment. Under no circumstances should you self-medicate, as this can cause various complications.
Fungus in the mouth is caused by yeast-like microorganisms of the genus Candida. Normally, the human microflora contains a certain amount of yeast fungi, the place of their localization is the skin, nasopharyngeal mucosa, intestines and other places. Under conditions favorable to reproduction, their number increases and candidiasis develops, which is popularly called thrush.
As they multiply, candida fungi change and take the form of elongated rods. Penetrating into the epithelium of the mucosa, they begin to destroy the surrounding tissue. The enzymes they secrete trigger the breakdown of proteins, fats and carbohydrates, resulting in the destruction of the mucous membrane.
Fungal diseases of the oral cavity develop against the background of a chemical imbalance, which leads to a decrease in general or local immunity. The following factors contribute to the proliferation of the pathogen:
- Decreased body defenses, immunodeficiency and lack of immune cells.
- Pregnancy, during which hormonal changes occur.
- Taking corticosteroid drugs that suppress the immune system.
- Long-term use of antibiotics, leading to disruption of the microflora.
- Hormonal imbalance due to the use of inappropriate oral contraceptives.
- Development of vitamin deficiency and dysbacteriosis. Fungal infections oral mucosa can develop with a deficiency of vitamins B, PP, C.
- Frequent stress and overwork weaken the body's immunity. Inadequate sleep poor nutrition, alcohol and smoking also increase the risk of infection.
- Injuries to the mucous membrane that can be caused removable dentures or braces bad habits pick your teeth.
- Chemotherapy. Patients who have undergone radiological treatment are also often exposed to lesions of this nature.
The fungus in the mouth forms a white, cheesy coating that accumulates on the surface of the mucous membrane. Initially, the lesion in the oral cavity appears as white grains. As the plaque grows, it forms in the form of plaques or a white film. Sometimes irritation spreads to the skin of the lips, forming flakes and scales. In the most advanced cases, it can cover the cheeks, gums, tongue, tonsils, and palate. The affected oral mucosa is accompanied by a burning sensation. The pain intensifies when swallowing food or saliva, and there is a feeling of a lump in the throat.
Small cracks, covered with a white coating, form in the corners of the mouth - mycotic seizures.
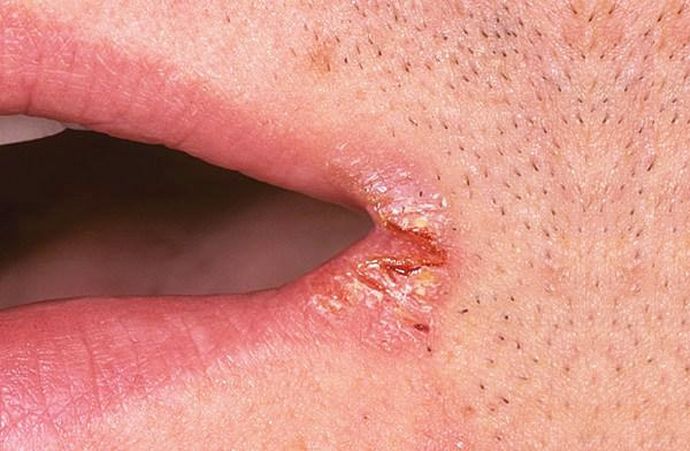
Seizures in the corners of the mouth
In the video, the doctor talks about the types and characteristics of seizures:
Fungal infection develops rapidly. Eating dead cells human body, she highlights toxic compounds and suppresses the immune system.
Types of fungal diseases
Dentists distinguish several types of diseases that are caused by fungus in the mouth.
Acute pseudomembranous candidiasis
This is the most common form of the disease caused by candida. Children are more susceptible to pathology infancy and adults with poor health. Infection of an infant occurs during childbirth from a sick mother. An infected child refuses to eat and becomes moody and lethargic.
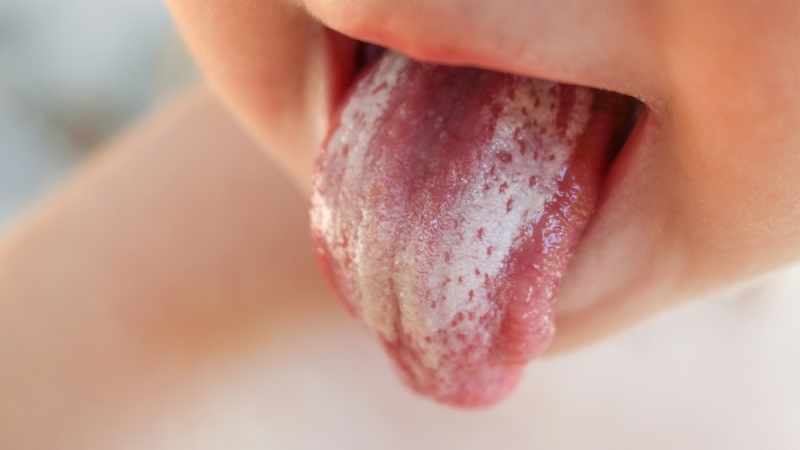

In adults, acute pseudomembranous candidiasis develops due to dysbacteriosis. The causes of the latter include antibiotics, hormonal drugs, diabetes mellitus, chemotherapy.
A mild form of candidiasis manifests itself in the form of weak, bad taste in the mouth, burning sensation when eating. The mucous membrane becomes covered with a white coating, which is easily removed.
At moderate form diseases plaque acquires gray-white color, has a dense consistency. The raid is amazing most mucous layer is difficult to remove, and underneath it a bleeding, erosive surface is revealed.
Severe candidal stomatitis is characterized by a general serious condition. A dark gray coating spreads over the entire surface of the mucosa, the plaque is scraped off with great difficulty, and the affected surface underneath bleeds heavily.
Pseudomembranous candidiasis can develop in chronic form. It is most often diagnosed in HIV-infected people and is difficult to treat. After diagnosis, it is necessary to prevent sore throat, herpes and diphtheria, since oral fungus often causes these complications. Treatment of fungus in the oral cavity is aimed at eliminating the infection and strengthening the immune system.
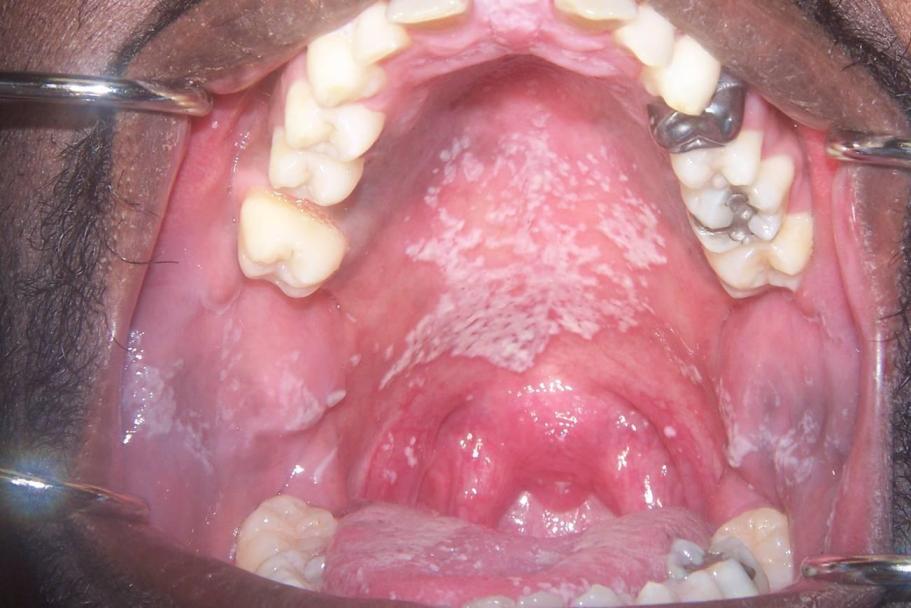
Acute atrophic candidiasis
A fungal disease of the oral cavity can develop independently or be a complication of thrush. The disease provokes long-term use antibiotics, hormones, wearing dentures. It often affects infants, people with chronic pathologies, sick diabetes mellitus. Infection can occur through direct contact with a patient, through household contact, or through common objects. Infection through unsterile medical instruments is possible.
In acute atrophic, symptoms manifest themselves in the form of a cheesy coating, burning, and dry mouth. Patients complain about severe pain, change in taste sensations. Treatment must be comprehensive. It is necessary to sanitize the oral cavity and create alkaline environment to kill fungi. For this purpose, antifungal drugs are prescribed medicines. It is necessary to rinse your mouth frequently with antiseptic solutions.
It is also used to treat damaged mucous membranes. wound healing ointments, balms, oils. Prescribe a diet that excludes flour products, sugar, potatoes and starchy foods. Hot, salty, spicy foods are not recommended. During treatment, you should switch to soft, smooth foods: liquid porridges, purees, pates, pureed soups.
Chronic atrophic candidiasis is often diagnosed in people who wear removable dentures. Signs and treatment are similar to acute form diseases. In such cases, the fungus affects the area of the palate under the prosthesis, forming pinpoint lesions.
If untreated, candidiasis forms diffuse erythema hard palate, multiple papules. Mycotic spots appear in the corners of the mouth. In this case, in addition to antifungal drugs, the doctor must prescribe immunotherapy. The affected areas under the prosthesis are lubricated with special solutions.
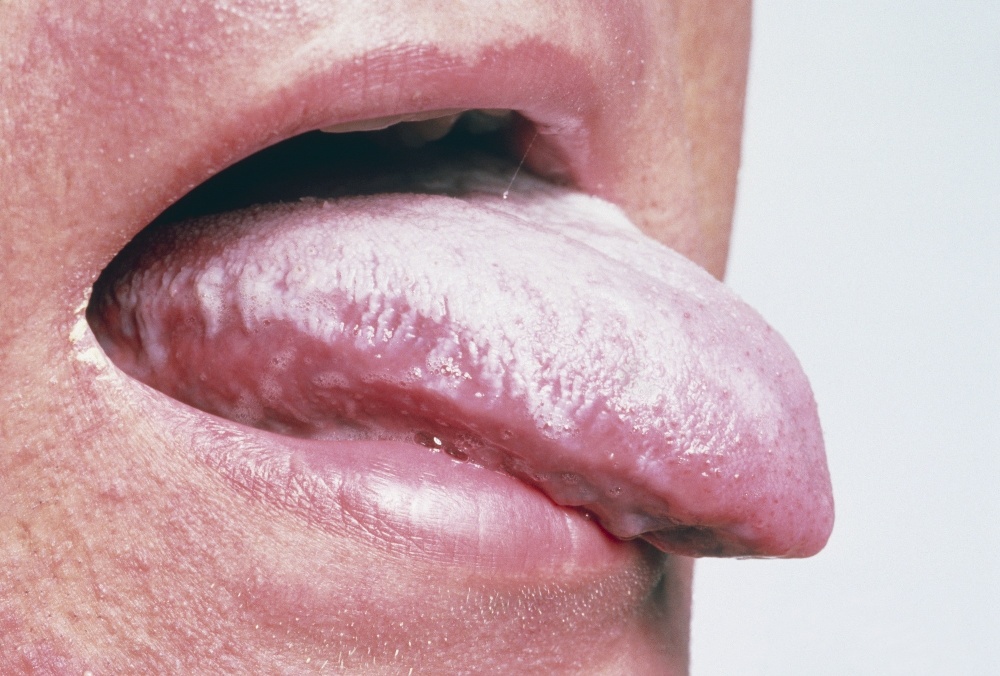

Chronic hyperplastic candidiasis
Characterized by tightly adherent transparent white plaques irregular shape and with an uneven bottom. The lesion affects the cheek area and the back of the tongue. Distinctive feature Hyperplastic candidiasis is that plaques cannot be removed from the mucous layer.
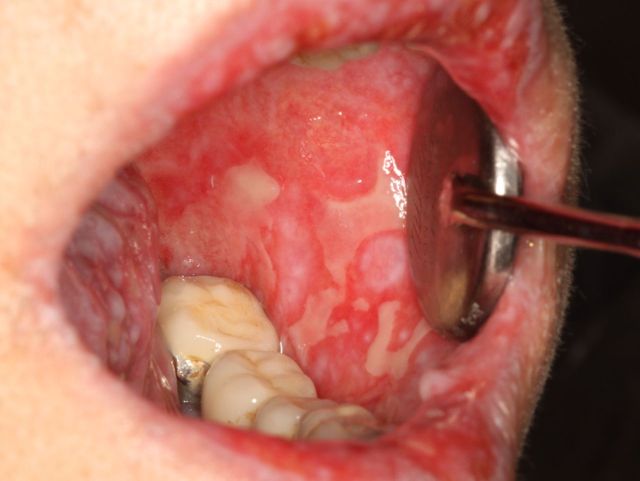
In the video, Elena Malysheva talks about candidiasis:
Diagnosis and treatment principles
For precise setting To make a diagnosis, a detailed medical history is collected, scrapings from the mucous membrane are examined to detect a pathogenic microorganism, and a general blood test is studied. If there is a fungus in the mouth, treatment is aimed at eliminating the causative agent of the disease and associated ailments, strengthening the immune system and the general tone of the body.
Fungal infections of the oral mucosa require special diet. Foods that provoke candidiasis are removed from the diet: sweets, yeast products, spicy, sour and salty foods.
Local treatment of a fungal infection consists of eliminating unpleasant symptoms and restoration of the mucous layer. To do this, ointments with analgesic and anti-inflammatory properties are used, and applications with a special solution are applied to the affected areas. Alkaline preparations are used for mouth rinsing and disinfectants. Competent consistent therapy will help overcome the process and prevent it from becoming chronic.
On average, the course of treatment takes 2-3 weeks. It is important to take the medicine for the entire prescribed time, even if the condition has noticeably improved. This is necessary to prevent relapses. After the therapy, a repeat microscopic examination is prescribed.
Folk remedies can serve as a complement to the main course. For example, for local treatment of the oral cavity, you can rinse with oil tea tree, which has strong antibacterial properties.

Also used for rinsing the mouth is a decoction of sage or Apple vinegar, diluted with warm water.
There are more than a million microorganisms in the human oral cavity, which strong immunity do not cause absolutely any discomfort to a person. But when creating favorable conditions pathogenic microflora begins to actively reproduce, causing various diseases. Yeast fungus in the mouth of the genus Candida loves an acidic environment. When there is a malfunction in the human body, these bacteria infect and destroy the tissues of the mucous membranes.
During their life activity, microorganisms produce special enzymes that cause painful sensations, dryness, burning, formation of ulcers at the site of the lesion. Thus, thrush develops. The fungus is most often localized on the tongue, lips, gums, palate, and the inside of the cheeks; treatment methods are selected taking into account the causes of the pathology.
Causes of fungus formation
Why does Candida fungus appear on the mucous membranes of the oral cavity, what are its main symptoms and methods of treatment?
How does fungus manifest itself in the mouth, what are the main symptoms? The first sign candidal stomatitis is the formation of a whitish coating on the mucous membranes of the oral cavity. With him
When removed, bleeding wounds remain. Raid on appearance resembles curdled milk or cottage cheese. In patients, it appears from the mouth stale smell, metallic taste in the mouth. Ulcers cause pain and burning during eating.
In newborns, stomatitis can be determined by plaque on the mucous membranes; children are capricious, eat and sleep poorly, and constantly put their hands in their mouths.
At untimely treatment stomatitis in young children, the fungus can affect the digestive tract and genitals.
In adults, erosions become infected, become inflamed and fester, and the plaque turns yellow. At the same time, body temperature rises and general health worsens.
Clinical forms of candidiasis
What types of oral fungus are there in humans, and how do their symptoms manifest themselves?
- Superficial mucosal candidiasis is characterized by the formation of wet erosions with a clearly defined contour. They are covered with a white coating on top; blisters and papules may appear in the lesion.
- Generalized stomatitis develops in people with acute immunodeficiency or advanced stage diseases. In addition to the oral cavity, they are affected skin head, corners of the mouth. First, scaly spots appear, which quickly become infected, become inflamed and fester, becoming covered with necrotic crusts. The disease negatively affects work digestive tract, upper respiratory tract, lowers the level of hemoglobin in the blood.
- Candidamicidae are secondary rashes caused by improper treatment pathology.
- Candidiasis of the corners of the mouth (jams), tongue, and red border of the lips is combined with damage to the mucous membranes of the oral cavity. Accumulates in the folds of the corners of the mouth white coating, after removal of which an eroded area remains. The cause of the disease is malocclusion and wearing dentures.
Treatment of oral fungus
 Candida fungus in the mouth causes a lot of discomfort and can lead to serious complications, so if symptoms of thrush appear, you should seek treatment from a dentist. For successful therapy, it is necessary to eliminate the causes of the disease.
Candida fungus in the mouth causes a lot of discomfort and can lead to serious complications, so if symptoms of thrush appear, you should seek treatment from a dentist. For successful therapy, it is necessary to eliminate the causes of the disease.
If you get sick Small child, you need to sanitize the baby’s dishes and hygiene items. You should not lick babies' nipples; bottles must be boiled in solution regularly baking soda.
If candidiasis is caused chronic diseases internal organs, appropriate treatment should be carried out by specialized specialists, carrying out comprehensive antibacterial therapy.
Treatment yeast fungus in the mouth aimed at suppression pathogenic microorganisms, normalization of microflora, wound healing, strengthening the immune system.
How to treat Candida fungus in the mouth? It is necessary to do antiseptic rinses of the mouth with solutions of Furacilin, Chlorhexedine, Miramistin, baking soda and salt 5-6 times a day. The use of decoctions gives a good therapeutic result medicinal herbs.
Erosions and ulcers should be treated with ointments and gels: Asepta, Solcaseril, Metrogyl. Useful for lubricating wounds essential oils fir, sea buckthorn, cloves, tea tree. It is important to take immunomodulatory treatment (Imudon, Echinacea) and a vitamin-mineral complex.
Fungus in the mouth is a consequence of the activity of strains of the Candida family. In small quantities, yeast-like microorganisms do not cause harm to humans. They live on the mucous membranes of the intestines, nasopharynx and on the surface of the skin.
Under certain conditions, pathogenic agents begin to multiply intensively. The body does not have time to cope with the colonies, and the fungi intensively inoculate all tissues.
Causes of oral candidiasis
Why is Candida activated in the oral cavity? Doctors talk about the impact various factors that provoke the development of the disease.
First of all, these are immunodeficiency states and weakness immune system after operations and serious pathologies. For women, pregnancy can be a provoking factor, because during this period the hormonal status the body, metabolism is disrupted and natural defenses deteriorate.
In addition, the causes of fungus in the mouth can be:
- Diabetes.
- Adrenal diseases.
- Radiation therapy.
- Dysbacteriosis of the intestines or vagina.
- Usage oral medications hormonal contraception.
- Long-term use of immunosuppressants, antibiotics, cytostatics, corticosteroids.
- Microtraumas of the oral cavity resulting from damaged teeth or malocclusion.
- Vitamin-depleted diet.
- Reduced or increased acidity gastric juice.
- Consumption of poorly prepared food and raw water.
- Foreign body in the oral cavity (wearing dentures or dentures).
All of these factors are to one degree or another associated with weakened immunity. In the presence of good health a person can be a carrier of a fungal infection and infect others. Thrush is transmitted by airborne droplets and through kisses, oral sex and handshakes.
Clinical signs of active fungus in the mouth
It is impossible to miss the first signs of candidiasis in the mouth. Thrush creates a lot of inconvenience, ranging from dryness and swelling of the affected mucosa to ulceration of the affected areas and swelling.
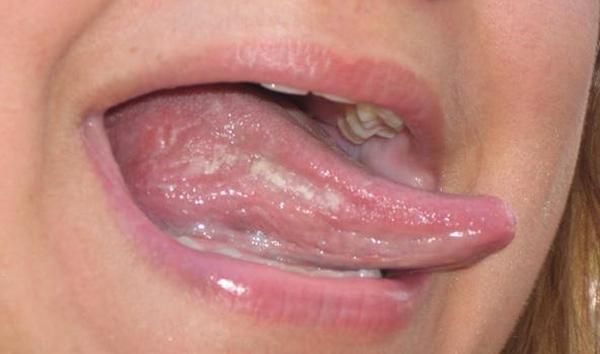
What are the symptoms of fungus in the mouth?
Mycotic seizure as a symptom of a fungal infection is small cracks in the corners of the lips. The process of their formation is accompanied by redness of the skin and the appearance of discomfort when opening your mouth.
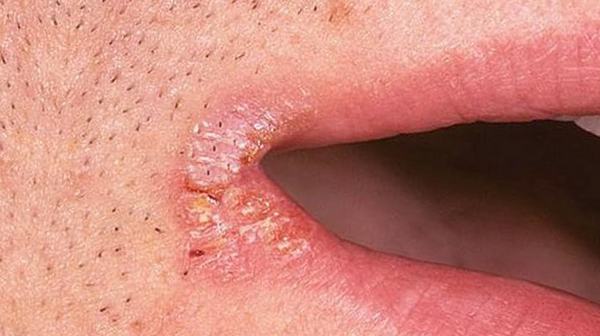
This feature is complemented profuse drooling and drooping of the corners of the lips. With candidomycosis, the jams become overgrown with a white coating or transparent scales. They can be removed without difficulty.
Milky films in the mouth with fungus first cover individual areas and then merge, forming large plaques. Pathological white elements appear on the gums, palate, tonsils, inner surface cheeks
Symptoms of fungus in the mouth in children do not differ from the “adult” candidiasis clinic. If a child can speak, he will tell you what is bothering him.

The baby reacts to soreness in the mouth by being capricious and refusing to feed. The baby's sleep is disturbed and the temperature rises slightly. With complicated thrush, the temperature rises to 39°C.
Treatment of dental candidiasis
Dentists and periodontists diagnose the disease, and they also prescribe treatment for fungus in the mouth. Features of therapy depend on the patient's medical history. In parallel, candidiasis must be treated accompanying illnesses Gastrointestinal tract, endocrine and circulatory system and other anomalies.

Dental thrush is treated with drugs from different groups:
Not only systemic, but also local treatment will help suppress Candida fungus in the mouth. External medications act only on the mucous membrane and stop the process of uncontrolled reproduction of mycotic strains. As a result, symptoms disappear and damage heals.
List of remedies for external treatment of thrush in the mouth:
Sanitation of the oral cavity is performed alkaline solutions and disinfectants - these are solutions of boric acid, borax, sodium bicarbonate and water solution Iodinol.
How to treat fungus in the mouth in adults using rinses? Solutions are used every 2 – 3 hours. Additionally, rinse your mouth after eating and before going to bed at night. Therapy lasts 7–14 days and is not interrupted if relief is felt earlier.
To prevent fungal infection of healthy tissues, candida vaccination is used. The drugs Pentoxyl and Methyluracil accelerate the synthesis of leukocytes and gamma globulins (these cells fight pathogens).
How to treat a child for thrush
From medications For fungus in a child's mouth, Fluconazole is used for treatment if the child is not allergic to its components.
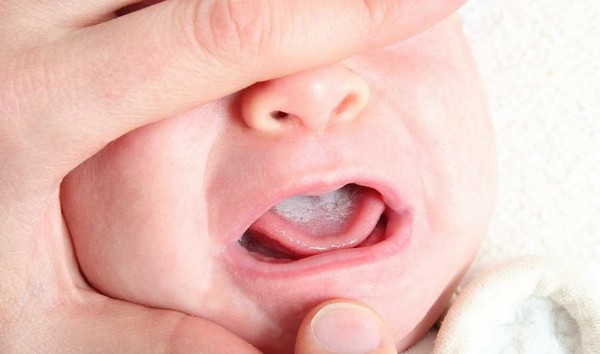
During the treatment of the baby, the mother also takes antifungal drug to avoid secondary infection of the baby through breast milk.
From 3 years of age, if there are signs of thrush in the mouth, children are given antiseptic lozenges and solutions are prepared for mouth rinsing:
- Salt with iodine.
- Urea peroxide.
- Benzocaine with glycerin and cetylperidine.
- Soda (the solution is prepared at the rate of 1 tsp per glass of warm boiled water). This product can be used to treat the mouth of newborns by moistening a piece of bandage and wiping the affected area.
P.S. You cannot self-medicate candidiasis, because it running forms significantly undermine the immune system and cause severe intoxication body. If you experience any discomfort in the mouth or white spots, you should consult a doctor - dentist, infectious disease specialist, mycologist.
