“Organoids of a eukaryotic cell” - Comparison of plant and animal cell. Ribosomes. Organoids for special purposes. Plastids are organelles characteristic only of plant cells. How can you figuratively call chloroplasts? Types of plastids. The goals are educational. What organelles are shown in these figures. Organelles of a eukaryotic cell. Cage Travel Worksheet. Developmental goals. Lesson objectives. Lysosome. Organelles of an animal cell.
“Structure of animal and plant cells” - Cell wall. Cell structure. Functions of lysosomes. Phospholipid. The structure of a plant and animal cell. Cell center. Functions of plastids. Glucose. Protein. Outer membrane. Vessels. Micrograph of the endoplasmic reticulum. Transcription. High-energy-intensive (macroenergetic) bonds. Lysosome. Ribosome. Golgi apparatus. Membrane functions. Function of the cell center. Presentation navigation. Cell. EPS functions.
“Structure of plant cell organelles” - Plant cell. Nucleus with chromosomes. Cell membrane. Endoplasmic reticulum. Cytoplasm. Mitochondria. Vacuole. Structure plant cell. The structure of the cell of a prokaryotic organism. Basic processes. Diagram of the structure of a plant cell. Golgi complex. Chloroplasts. Organoids. Discovery of cells.
"Structure of the human cell" - Internal environment body. Organic substances. Inorganic substances. Thread-like formations. The cell is covered with a membrane. Cell. Cytology. Cytoplasm. The human body. Questions after the paragraph. Chemical composition of the cell. Life properties cells.
“Cellular structure of plants” - Basic structural unit plants. Chromoplasts. Core. Chloroplasts. Leukoplasts. Cytoplasm. Cell growth. Cell wall. Vacuoles. Wood cells. Plastids. Strength of cell membranes. Cell (plasma) membrane. Vital activity of the cell. Cellular structure plants. Cell division. Plant cell. Cell. Cell organelles.
“Structural features of eukaryotic cells” - Viruses. Mitochondria. Vacuoles. The structure of a eukaryotic cell. Dictionary. Inclusions. Leeuwenhoek. R. Virchow. Endoplasmic reticulum. From the history of cytology. Diversity of cells. Mitochondria. Schleiden. Organoids. Cell structure. Cytoplasm. Core. Cells that do not have a formed nucleus. Nucleolus. Variety of viruses. Cellular center. The structure of a prokaryotic cell. Diversity and structural features of cells.
figure with numbers 1, 2, 3 and what functions do they perform?
Response elements:
1) 1 – protein molecules, they perform functions: structural and transport;
2) 2 – bimolecular layer of lipids, delimits the internal contents of the cell and ensures the selective supply of substances;
3) 3 – glycocalyx (glycoprotein complex), ensures the connection of similar cells, performs a receptor (signaling) function.
4.Name the plant cell organelle shown in the figure, its structures, indicated by numbers 1-3, and their functions. ( drawing-scheme chloroplast)
Response elements:
1) the organelle depicted is a chloroplast;
2) 1 - grana thylakoids, participate in photosynthesis;
3) 2 - DNA, 3 - ribosomes, participate in the synthesis of the chloroplast’s own proteins.
5.What stages of gametogenesis are indicated in the figure by letters A, B and C? What set of chromosomes do cells have at each of these stages? What specialized cells does this process lead to the development of? (stages of gametogenesis - drawing - diagram)
Response elements:
1) A - stage (zone) of reproduction (division), diploid cells;
2) B - stage (zone) of growth, diploid cell;
3) B - stage (zone) of maturation, the cells are haploid, sperm develop.
6.Look at the cells shown in the figure. Determine which letters represent prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Provide evidence for your point of view.
Response elements:
1) A - prokaryotic cell, B - eukaryotic cell;
2) the cell in Figure A does not have a formed nucleus, its hereditary material is represented by a ring chromosome;
3) the cell in Figure B has a formed nucleus and organelles.
7. Find errors in the given text. Indicate the numbers of the sentences in which errors were made and correct them.
1. Coelenterates are three-layer multicellular animals
2. They have a gastric or intestinal cavity. 3. The intestinal cavity includes stinging cells. 4. Coelenterates have a reticular (diffuse) nervous system. 5. All coelenterates are free-swimming organisms.
Response elements:
1) 1 - coelenterates - two-layer animals;
2) 3 - stinging cells are contained in the ectoderm, and not in intestinal cavity;
3) 5 - among the coelenterates there are attached forms.
8. Find errors in the given text. Indicate the numbers of the sentences in which errors were made and correct them.
1. Flatworms- these are three-layered animals. 2. The phylum Flatworms include white planaria, human roundworm and liver flukes 3. Flatworms have an elongated, flattened body. 4. They are well developed nervous system. 5. Flatworms are dioecious animals that lay eggs.
Response elements:
errors were made in the sentences:
1)2 - the human roundworm is not classified as a Flatworm; it is a Roundworm;
2) 4- in flatworms the nervous system is poorly developed;
3) 5 - Flatworms are hermaphrodites.
C1. What is the role of chemosynthetic bacteria in ecosystems?
Answer:
1) Form organic substances from inorganic ones;
2) They are classified as producers and in ecosystems they form the first link in the food chain.
C1. Which milk, sterilized or freshly milked, will sour faster under the same conditions? Explain your answer.
Answer:
1) freshly milked milk will sour faster, since it contains bacteria that cause fermentation of the product;
2) when milk is sterilized, the cells and spores of lactic acid bacteria die and the milk lasts longer.
C1. To which systematic group include bacteriophages? What is the peculiarity of their metabolism?
Answer:
1) bacteriophages belong to the group of viruses, non-cellular life forms;
C1. What is the role of bacteria in the cycle of substances?
Answer:
1) heterotrophic bacteria - decomposers decompose organic substances into minerals, which are absorbed by plants;
2) autotrophic bacteria - producers synthesize organic substances from inorganic ones, ensuring the circulation of oxygen, carbon, and nitrogen.
C2. Look at the cells shown in the figure. Determine which letters represent prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Provide evidence for your point of view.
Answer:
1) A – prokaryotic, B – eukaryotic cell;
2) the cell in Figure A does not have a formed nucleus, its hereditary material is represented by a ring chromosome;
3) the cell in Figure B has a formed nucleus and organelles.
C3. How do bacteria differ from organisms in other kingdoms of life? Please indicate at least 3 differences.
Answer:
1) there is no formed core, nuclear envelope;
2) a number of organelles are missing: mitochondria, EPS, Golgi apparatus...
3) have one ring chromosome.
C3. What is the significance of bacteria in nature? Specify at least 4 values.
Answer:
1) participate in the cycle of substances, performing the role of all functional groups (producers, consumers and decomposers);
2) participate in soil formation and maintenance of soil fertility;
3) are pathogens of plant and animal diseases;
4) enter into symbiosis.
C2.
1. Cellular organisms divided into 2 groups: prokaryotes and eukaryotes.
2. Prokaryotes – prenuclear organisms. 3. Prokaryotes include single-celled organisms: bacteria, algae, protozoa. 4. Only multicellular organisms are classified as eukaryotes. 5. Prokaryotes obtain energy for life through the process of oxidation organic matter in mitochondria. 6. A group of prokaryotes (Cyanobacteria) use solar energy in the process of photosynthesis to form organic substances from inorganic ones.
Answer:
1) 3 – prokaryotes include bacteria, but do not include algae and protozoa;
2) 4 – eukaryotes include all nuclear organisms, both unicellular and multicellular;
3) 5 – prokaryotes do not have mitochondria, so in them the process of oxidation of organic substances takes place on membrane folds located in the cytoplasm.
C2. Find errors in the given text. Indicate the numbers of the sentences in which they are made and explain them.
1. Bacteria, like all living organisms, undergo metabolism and energy conversion. 2. According to the method of nutrition, they are divided into autotrophs and heterotrophs. 3. Chemotrophic bacteria, synthesizing organic substances from inorganic ones, use the energy of the sun. 4. Photosynthesis in autotrophic bacteria occurs in chloroplasts, like in plants. 5. All bacteria breathe oxygen.
Answer:
1) 3 – chemotrophs that use energy rather than light energy chemical bonds;
2) 4 – there are no chloroplasts in the cells of autotrophic bacteria;
3) 5 – anaerobic bacteria do not use oxygen for breathing.
C2. Name the object shown in the picture. What are the features of its structure and life activity?
C 2 No. 15980. Write down the names of the parts of an animal cell shown in the diagram. In your answer, indicate the part number and its name; there is no need to redraw the cell diagram.
1. digestive vacuole
2. cytoskeleton OR microtubules OR microfilaments
3. membrane
4. rough EPS OR granular EPS
5. smooth EPS
6. lysosome
7. Golgi complex
8. ribosome
9. mitochondrion
10. chromatin OR chromosome
11. nucleus OR nuclear sap OR nuclear matrix
12. nucleolus
C 2 No. 16030. Write down the names of the parts of the plant cell shown in the diagram. In your answer, indicate the part number and its name; there is no need to redraw the cell diagram.
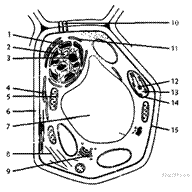
1. chromatin OR chromosome
2. nucleus OR nuclear matrix OR nuclear juice
3. nucleolus
4. smooth EPS
5. mitochondrion
6. membrane OR cell wall
7. tonoplast OR central vacuole
8. cytoskeleton OR microtubules OR microfilaments
9. dictyosome (Golgi apparatus)
10. plasmodesma
11. rough EPS OR granular EPS
12. thylakoids OR grana
13. stroma
14. chloroplast
15. membrane
C3. Name at least 3 differences in the structure of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
Answer:
in prokaryotic cells
1) the nuclear substance is not separated from the cytoplasm by a membrane;
2) one circular DNA molecule – nucleoid;
3) most organelles are missing, except ribosomes.
C4. What is the evidence for the unity of the organic world? Provide at least 4 pieces of evidence.
Answer:
1) cell – a unit of structure and vital activity of all organisms;
2) similarity chemical composition cells;
3) development of organisms from one cell;
4) versatility genetic code, the principle of storage and implementation of hereditary information.
C4. Why is a cell considered structural and functional unit alive?
Answer:
1) Living systems consist of cells.
2) The cell can be part multicellular organism or an independent organism.
3) Living systems develop from a single cell.
C4. Prove that the cell is an open system.
Answer:
1) The cell participates in constant exchange of substances and energy with environment.
2) The cell responds to signals external environment and returns to its original state. Her reactions are reversible.
3) The cell is capable of regulating its chemical composition.
C3. Reveal at least 3 functions of proteins located in the plasma membranes of cells.
Answer:
1) construction – included in membranes;
2) transport - transport molecules and ions across the membrane;
3) enzymatic - located on the membrane and accelerate metabolic reactions.
C 2 No. 14141. What processes are shown in Figures A and B? Name the cell structure involved in these processes. What transformations will next occur with the bacterium in Figure A?
1) A - phagocytosis (capture of solid particles);
B - pinocytosis (capture of liquid droplets);
2) Participates in the cell (plasma) membrane;
3) A phagocytic vesicle has formed, which, having connected with the lysosome, forms a digestive vacuole - the bacterium will be digested (lysis - will undergo splitting) - the resulting monomers will enter the cytoplasm.
C4. By what routes do substances enter the cell? What is the mechanism of their arrival?
Answer:
1) Phagocytosis - absorption, capture of solid particles by the cell membrane and their subsequent digestion.
2) Pinocytosis - absorption of liquids by the cell membrane;
3) Diffusion and osmosis are the processes of substances flowing from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration. A special case of osmosis is the penetration of substances through a semi-permeable membrane.
4) Active transport - the transfer of substances against a concentration gradient, which occurs with the expenditure of energy.
C3. By what features can you distinguish a plant cell from an animal cell? Please indicate at least 3 characteristics.
Answer:
1) has a dense cell wall from cellulose;
2) contains chloroplasts;
3) contains one or more vacuoles with cell sap.
C4. How do ribosomes form in eukaryotic cells?
Answer:
1) In eukaryotic cells, ribosomes are formed in the nucleolus.
2) r-RNA is synthesized on DNA, to which proteins are then attached.
3) Subparticles of the ribosome leave the nucleus into the cytoplasm, and here the formation of full-fledged ribosomes is completed.
C4. What features of chromosomes ensure the transmission of hereditary information?
Answer:
C1.In a comparative study of pancreatic and skeletal muscle cells, a difference was found in percentage structures of the Golgi apparatus. Explain these differences in terms of its function.
1) the Golgi apparatus is larger in pancreatic cells;
2) enzymes are formed in the pancreas, which accumulate in the Golgi apparatus, are removed from it into the ducts and are used in digestion
C2. Name the plant cell organelle shown in the figure, its structures indicated by numbers 1-3, and their functions.
Answer:
1) the organelle depicted is a chloroplast;
2) 1 – granal thylakoids, involved in photosynthesis;
3) 2 – DNA, 3 – ribosomes, participate in the synthesis of the chloroplast’s own proteins.
C2. Which organelle is shown in the diagram? Which parts of it are marked with numbers 1, 2 and 3? What process occurs in this organelle?
Answer:
1) Mitochondria.
2) 1 - outer membrane, 2 - mitochondrial matrix, 3 - cristae, inner membrane.
3) An energy process takes place here with the formation of ATP molecules.
C3. What role do mitochondria play in the human body? Which tissue - muscle or connective tissue - contains more mitochondria? Explain why.
Answer:
1) mitochondria - cell organelles in which intracellular final oxidation (respiration) occurs;
2) ATP is formed - a universal source of energy in the cell;
3) muscle contains more mitochondria, since muscle contraction requires a large number of energy.
C4. total weight mitochondria in relation to cell mass various organs rats is: in the pancreas - 7.9%, in the liver - 18.4%, in the heart - 35.8%. Why do the cells of these organs have different mitochondrial content?
Answer:
1) Mitochondria are the energy stations of the cell; ATP molecules are synthesized and accumulated in them;
2) intensive work of the heart muscle requires a lot of energy, therefore the content of mitochondria in its cells is the highest;
3) in the liver the number of mitochondria is higher compared to the pancreas, since it has a more intense metabolism.
C4. It is known that the Golgi apparatus is especially well developed in glandular cells (adrenal glands, salivary glands, pancreas). Explain this fact using knowledge about the functions of this organelle in the cell.
Answer:
1) Enzymes are synthesized in gland cells, which accumulate in the cavities of the Golgi apparatus;
2) in the Golgi apparatus, enzymes are packaged in the form of vesicles;
3) from the Golgi apparatus, enzymes are carried into the glandular duct.
C4. What similarities between mitochondria and prokaryotes allowed us to put forward the symbiotic theory of the origin of the eukaryotic cell?
Answer:
1) They have two completely closed membranes. In this case, the outer one is similar to the membranes of vacuoles, the inner one is similar to bacteria.
2) They reproduce by binary fission (and sometimes divide independently of cell division).
3) Genetic material - circular DNA, not associated with histones, have their own protein synthesis apparatus - ribosomes, etc. Ribosomes are of the prokaryotic type.
C4. Why cannot mitochondria, chloroplasts and other cell organelles be considered a structural and functional unit of living things?
Answer:
1) Metabolism and energy conversion - the basis of life; all organelles participate in metabolism.
2) A single organelle does not provide the entire metabolism.
3) An organoid cannot be considered a living unit.
C4. Why are mitochondria called the “powerhouses” of cells?
Answer:
1) During the oxidation of organic substances in mitochondria, energy is released.
2) This energy is used for the synthesis of ATP and is stored in them.
3) ATP energy is used for all life processes.
C1. Ribosomes from different cells, the entire set of amino acids and identical molecules of mRNA and tRNA, created all the conditions for protein synthesis. Why will one type of protein be synthesized on different ribosomes in a test tube?
Answer:
1) the primary structure of a protein is determined by the sequence of amino acids;
2) the templates for protein synthesis are identical mRNA molecules, in which the same primary protein structure is encoded.
“3D drawings on asphalt” - In his youth, Kurt Wenner worked as an illustrator at NASA, where he created the initial images of future spaceships. 3d drawings on asphalt. Philip Kozlov is the first Russian Madonnari. Kurt began creating his first works at the age of 16 in Santa Barbara, where he became addicted to street art.
“Editing pictures” - Selected area. Figure Flip/rotate Left to right Top to bottom ok Rotate by angle. Shift. Circle Square Straight line. Drawing attributes width height Ok Magnification of the drawing: Technology for creating a drawing. Clear picture Select area to be deleted Delete. Deleting a drawing. 1. Select the required area, select an arbitrary area 2. Copy.
“Plant world” - Drought-resistant plants. Early flowering plants. Vegetable world steppes. Vegetation map of the Rostov region. Color it and remember it. Schrenk's tulip. Vegetation of the steppes. We and the world. Map natural areas Eurasia.
“Flora and fauna of Antarctica” - Amazing phenomena in Antarctica “Rusty Falls” “Red Snow”. Seals. Sea Elephant. Emperor penguin. Imprints of ancient ferns. Leopard seal. Reds sea urchins. Rotifer. Predator birds Skua Albatross. Krill. Make a list of protected areas and protected species. Plankton.
“Computer drawing” - Dmitry Isidorovich Mitrokhin. Intellectual warm-up. The result of the lesson is the crossword puzzle “Mill”. Goal: Lesson topic: Graphics. Conclusion. Lesson plan. The main expressive means of drawing is line. Born in 1884 in Yeisk, Krasnodar Territory. this is the artist's weapon. From the French crayon - a tool for drawing and writing in the form of a rod or stick.
