The history of the discovery of an amazing and such a vitally important phenomenon as photosynthesis is rooted deep in the past. More than four centuries ago, in 1600, the Belgian scientist Jan Van - Helmont set up a simple experiment. He placed a willow branch in a bag containing 80 kg of earth. The scientist recorded the initial weight of the willow, and then for five years watered the plant exclusively with rainwater. What was the surprise of Jan Van - Helmont when he re-weighed the willow. The weight of the plant increased by 65 kg, and the mass of the earth decreased by only 50 grams! Where did the plant get 64 kg 950 g of nutrients for the scientist remained a mystery!
The next significant experiment on the path to the discovery of photosynthesis belonged to the English chemist Joseph Priestley. The scientist put a mouse under the cap, and after five hours the rodent died. When Priestley placed a sprig of mint with the mouse and also covered the rodent with a cap, the mouse remained alive. This experiment led the scientist to the idea that there is a process opposite to breathing. Jan Ingenhaus in 1779 established the fact that only the green parts of plants are capable of releasing oxygen. Three years later, the Swiss scientist Jean Senebier proved that carbon dioxide, under the influence of sunlight, decomposes in the green organelles of plants. Just five years later, the French scientist Jacques Bussingault, conducting laboratory research, discovered the fact that the absorption of water by plants also occurs during the synthesis of organic substances. A landmark discovery in 1864 was made by the German botanist Julius Sachs. He was able to prove that the volume of carbon dioxide consumed and oxygen released occurs in a ratio of 1: 1.
Photosynthesis is one of the most important biological processes
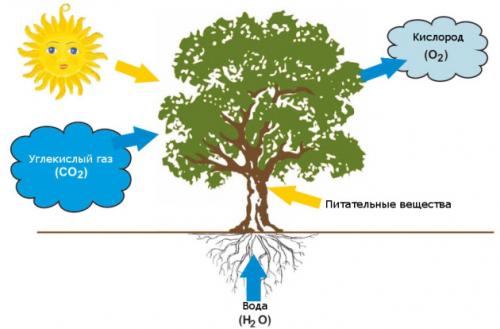
In scientific terms, photosynthesis (from ancient Greek φῶς - light and σύνθεσις - connection, binding) is a process in which organic substances are formed from carbon dioxide and water in the light. The main role in this process belongs to photosynthetic segments.
Speaking figuratively, the leaf of a plant can be compared with a laboratory, the windows of which face the sunny side. It is in it that the formation of organic substances occurs. This process is the basis for the existence of all life on Earth.
Many will reasonably ask the question: what do people who live in the city breathe, where not only trees, and you can’t find blades of grass during the day with fire. The answer is very simple. The fact is that land plants account for only 20% of the oxygen released by plants. Algae play a major role in the production of oxygen into the atmosphere. They account for 80% of the oxygen produced. In the language of numbers, both plants and algae release 145 billion tons (!) of oxygen into the atmosphere every year! No wonder the world's oceans are called the "lungs of the planet."
The general formula for photosynthesis is as follows:
Water + Carbon Dioxide + Light → Carbohydrates + Oxygen
Why do plants need photosynthesis?

As we have understood, photosynthesis is a necessary condition for the existence of man on Earth. However, this is not the only reason why photosynthetic organisms actively produce oxygen into the atmosphere. The fact is that both algae and plants annually form more than 100 billion organic substances (!), which form the basis of their life activity. Remembering the experiment of Jan Van Helmont, we understand that photosynthesis is the basis of plant nutrition. It has been scientifically proven that 95% of the crop is determined by organic substances obtained by the plant in the process of photosynthesis, and 5% - those mineral fertilizers that the gardener introduces into the soil.
Modern summer residents focus on the soil nutrition of plants, forgetting about its air nutrition. It is not known what kind of harvest gardeners could get if they were attentive to the process of photosynthesis.
However, neither plants nor algae could produce oxygen and carbohydrates so actively if they did not have an amazing green pigment - chlorophyll.
The secret of the green pigment

The main difference between plant cells and cells of other living organisms is the presence of chlorophyll. By the way, it is he who is the culprit of the fact that the leaves of plants are colored precisely in green. This complex organic compound has one amazing property: it can absorb sunlight! Thanks to chlorophyll, the process of photosynthesis becomes possible.
Two stages of photosynthesis
In simple terms, photosynthesis is a process in which water and carbon dioxide absorbed by a plant in the light with the help of chlorophyll form sugar and oxygen. Thus, inorganic substances are miraculously transformed into organic ones. The resulting sugar is the energy source of plants.
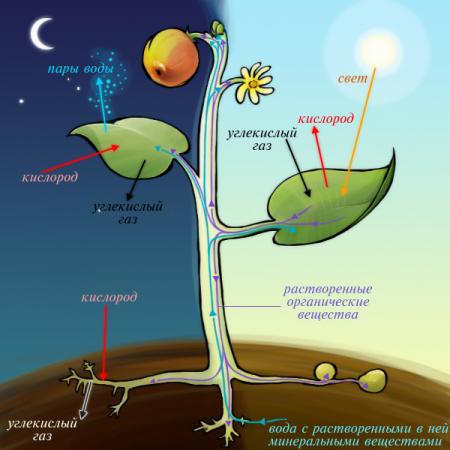
Photosynthesis has two stages: light and dark.
Light phase of photosynthesis
Occurs on thylakoid membranes.
Thylakoid are structures bounded by a membrane. They are located in the stroma of the chloroplast.
The order of events of the light stage of photosynthesis:
- Light hits the chlorophyll molecule, which is then absorbed by the green pigment and brings it into an excited state. The electron included in the molecule goes to a higher level, participates in the synthesis process.
- There is a splitting of water, during which protons under the influence of electrons turn into hydrogen atoms. Subsequently, they are spent on the synthesis of carbohydrates.
- At the final stage of the light stage, ATP (adenosine triphosphate) is synthesized. This is an organic substance that plays the role of a universal energy accumulator in biological systems.
Dark phase of photosynthesis
The site of the dark phase is the stroma of chloroplasts. It is during the dark phase that oxygen is released and glucose is synthesized. Many will think that this phase got such a name because the processes taking place within this stage are carried out exclusively at night. Actually, this is not entirely true. Glucose synthesis occurs around the clock. The fact is that it is at this stage that light energy is no longer consumed, which means that it is simply not needed.
Importance of photosynthesis for plants

We have already identified the fact that plants need photosynthesis no less than we do. It is very easy to talk about the scale of photosynthesis in the language of numbers. Scientists have calculated that only land plants store as much solar energy as 100 megacities could use up within 100 years!
Plant respiration is a process opposite to photosynthesis. The meaning of plant respiration is to release energy in the process of photosynthesis and direct it to the needs of plants. In simple terms, harvest is the difference between photosynthesis and respiration. The more photosynthesis and the lower respiration, the greater the harvest, and vice versa!
Photosynthesis is the amazing process that makes life possible on Earth!
