A healthy intestine contains various bacteria that take part in the processing and assimilation of food, protecting the body. Imbalance of beneficial and opportunistic bacteria can lead to gastrointestinal dysbacteriosis, which is expressed by such diseases as flatulence, diarrhea, constipation or other intestinal disorders.
At the first symptoms of dysbacteriosis, the doctor prescribes an examination, the patient submits the material, and deciphering the analysis for dysbacteriosis in adults determines the composition of the microflora.
Main indicators in the analysis sheet
The list of analyzes for bakposev contains a lot of narrow-profile information, and a specialist's consultation is often required to decipher it. The table indicates the name of the bacterium, the result of the analysis and the norm. The doctor, comparing the indicators, draws a conclusion about the condition and functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, establishes the fact of the development of dysbacteriosis and imbalance of microflora.
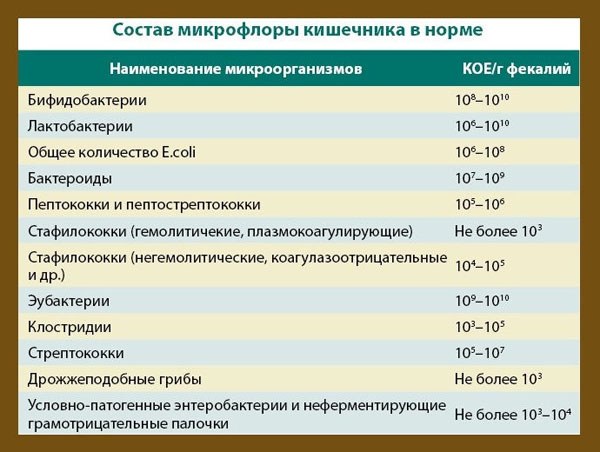
The decoding of laboratory tests for the development of dysbacteriosis in adults contains a list of all major bacteria, including those that should not be present in the body.
bifidobacteria
The normal content of these beneficial bacteria is at least 95% or higher. Bifidobacteria are responsible for the absorption of vitamins, are involved in the breakdown of food, its digestion and absorption of trace elements.
Bacteria also play another important role - they remove toxins by stimulating the intestinal walls.
lactobacilli
Sour-milk viruses, or lactobacilli, contribute to the production of lactic acid and are necessary for the full functioning of the intestine. The normal ratio of the content of lactobacilli is 5%.
Escheria coli or Escherichia coli
Despite the low content, the bacterium is necessary to maintain the microflora of the gastrointestinal tract.
E. coli ferments lactose, prevents an increase in the number of opportunistic microorganisms, supports the vital activity of bifidobacteria in the intestine, promotes the production of B vitamins, the absorption of calcium and iron.
The normal content of Escherichia coli is 1%
Bacteroids
Anaerobic microorganisms that do not form spores. Bacteroides are involved in the breakdown of bile acids, digestion of food, and lipid metabolism processes.
These bacteria are sometimes mistakenly referred to as harmful trace elements, after birth they gradually inhabit the human body, but their role in the digestive tract is not fully understood.
Enterococci
Gram-positive aerobes, anaerobes and cocci that colonize the small and large intestines are involved in the fermentation of carbohydrates and prevent the reproduction of pathogenic or opportunistic microorganisms.
Despite the fact that enterococci are causative agents of various diseases, a small amount of them is necessary for a healthy body.
Pathogenic microbes
Pathogenic bacteria include Salmonella, Shigella. Penetrating into the intestine, microorganisms provoke the development of infectious intestinal diseases. Their content, even in small quantities, can cause urgent hospitalization.
Staphylococci
Epidermal staphylococcus, similar to enterococci, belongs to the group of opportunistic bacteria, is part of the microflora of a healthy intestine. Its percentage is 25%.
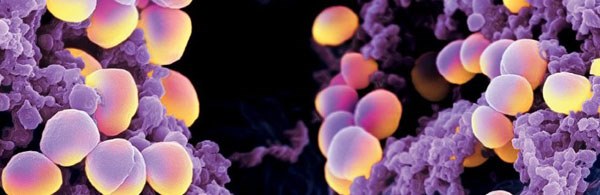
Staphylococcus aureus belongs to the microbes of the external environment, the slightest ingestion of these microorganisms into the intestines can cause a serious disorder, accompanied by pain in the abdomen, vomiting or diarrhea.
Fungi
Yeast-like bacteria of the genus Candida are contained in the microflora of a healthy intestine in a small amount, which can increase after taking antibiotics.
Indicators of normal and pathogenic microflora
Having studied the laboratory test sheet, even without a medical education, you can determine the state of the intestinal microflora, based on the norms of bacteria in the intestine
Different laboratories have a slightly different concept of "norm".
But there are basic standards that you can focus on when deciphering the results of laboratory analysis for dysbacteriosis in adults:
- Bifidobacteria: 108 - 1010.
- Lactobacilli: 106 - 108.
- E. coli: 106 - 108.
- Bacteroids: 107 - 108.
- Enterococci: 105 - 108.
- Pathogenic enterobacteria: absent.
- Peptostreptococci: 105 - 106.
- Saprophytic staphylococci: ≤104.
- Pathogenic staphylococci: absent.
- Candida: ≤104.
Symptoms of dysbacteriosis
Symptoms of dysbacteriosis can be different. Specialists establish a preliminary diagnosis when a patient has at least three signs for 10 days or longer.
Prolonged pain in the abdomen and intestines is the first signal of the development of the disease, a violation of the microflora causes infectious diseases, and in some cases ulcers.
With dysbacteriosis, food is not digested properly, which leads to intoxication and such a symptom as an unpleasant aftertaste in the mouth, which is not associated with the use of various products.
It is important to know! Improper food processing prevents the full absorption of beneficial trace elements, which can provoke intense weight loss for no apparent reason.
Flatulence is also considered one of the signs of the disease, but only in cases where gas formation is permanent and not associated with the use of certain foods. A large formation of gases in the intestine against the background of dysbacteriosis causes severe physical discomfort.

Intestinal imbalance is often expressed as a regular violation of the stool, which subsequently leads to diseases such as anal fissures or hemorrhoids.
Severe discomfort in the stomach (voluntary bubbling, rumbling), as well as general malaise, is a natural reaction of a weakened organism to the development of intestinal dysbacteriosis. It should be taken into account that drowsiness and headaches are not a reason to make a diagnosis, but, in combination with other symptoms, this will become an additional confirmation of the disease.
How to submit material
Before taking material for tests for dysbacteriosis in adults or children, must be familiar with the rules, otherwise the decryption will show erroneous data.
Let's consider the main ones:
- Stop taking probiotics and eubiotics 4 weeks before donating the material.
- Antibiotics are prescribed after the study or a day after administration.
- 4 days before the collection of the material, all drugs that can affect the microflora of the gastrointestinal tract, with the exception of the necessary ones, as well as rectal suppositories, should be abandoned.
If in doubt, it is better to visit a specialist and consult which medications can be temporarily excluded.
- Before collecting the material, it is forbidden to use any creams, give an enema or use other stimulants.
Defecation should be natural
- During stool collection, urine must not enter the material container.
- To avoid research errors, it is recommended to use only sterile containers. The lid of the jar must be tightly closed so that other microorganisms do not get inside.
- Only fresh material is suitable for analysis, it must be submitted to the laboratory no later than 3 hours later.
- Do not store the material for 5 hours or more, and do not freeze it.

It is important to know! When collecting material on a diaper or towel, the fabric must be ironed with a hot iron, this is necessary to sterilize the surface.
How accurate is the analysis
The maximum accuracy of the analysis is guaranteed by compliance with all the rules for collecting material, but there are some nuances. Only those microorganisms that move freely in the intestines enter the feces. The study of the mucous membrane will give a more accurate "picture" of the state of the microflora, because it contains several times more different bacteria.
Among microorganisms there are also so-called "anaerobes", that is, bacteria that exist without oxygen. Naturally, when collecting material, most of these bacteria die, in fact, there are much more of them than the decoding of the analysis for dysbacteriosis in adults shows.

In clinics, it is often recommended to donate material immediately after collection, despite the fact that in practice it is difficult, you should not neglect this rule. The longer the feces are stored, the less accurate the analysis will be.. Some of the bacteria will inevitably die under the influence of the external environment.
It is allowed to take tests again, to compare readings or when there is doubt about their accuracy. You can use the services of research tests for dysbacteriosis in adults in different laboratories, but from each you need to take a ready-made transcript indicating the norm.
How to treat dysbacteriosis in adults, restoration of intestinal microflora. Learn useful information from the video:
Intestinal dysbacteriosis: concept and treatment. Watch the video consultation of a specialist:
Online transcription of stool analysis. Watch informative video:
