These structures, despite the unity of origin, have significant differences.
General plan of cell structure
Considering cells, it is necessary first of all to recall the basic laws of their development and structure. They have common structural features, and consist of surface structures, cytoplasm and permanent structures - organelles. As a result of vital activity, organic substances, which are called inclusions, are deposited in them in reserve. New cells arise as a result of the division of maternal ones. During this process, two or more young structures can be formed from one initial structure, which are an exact genetic copy of the original ones. Cells that have the same structural features and functions are combined into tissues. It is from these structures that the formation of organs and their systems occurs.
Comparison of plant and animal cells: table
On the table you can easily see all the similarities and differences in the cells of both categories.
| Signs for comparison | plant cell | animal cell |
| Features of the cell wall | Consists of cellulose polysaccharide. | It is a glycocalyx-thin layer consisting of compounds of proteins with carbohydrates and lipids. |
| The presence of a cell center | It is found only in the cells of lower algae plants. | Found in all cells. |
| The presence and location of the nucleus | The core is located in the near-wall zone. | The nucleus is located in the center of the cell. |
| Presence of plastids | The presence of plastids of three types: chloro-, chromo- and leucoplasts. | None. |
| The ability to photosynthesis | Occurs on the inner surface of chloroplasts. | Not capable. |
| Feeding method | Autotrophic. | Heterotrophic. |
| Vacuoles | They are large | Digestive and |
| Reserve carbohydrate | Starch. | Glycogen. |
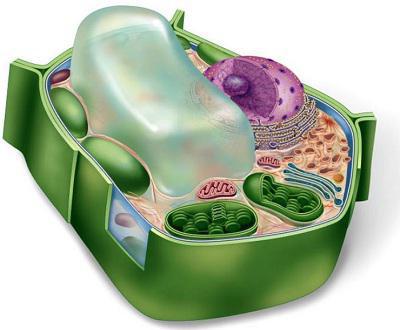
Main differences
Comparison of plant and animal cells indicates a number of differences in the features of their structure, and hence the processes of life. So, despite the unity of the general plan, their surface apparatus differs in chemical composition. Cellulose, which is part of the cell wall of plants, gives them a permanent shape. Animal glycocalyx, on the contrary, is a thin elastic layer. However, the most important fundamental difference between these cells and the organisms they form lies in the way they feed. Plants have green plastids called chloroplasts in their cytoplasm. A complex chemical reaction takes place on their inner surface, converting water and carbon dioxide into monosaccharides. This process is possible only in the presence of sunlight and is called photosynthesis. The by-product of the reaction is oxygen.
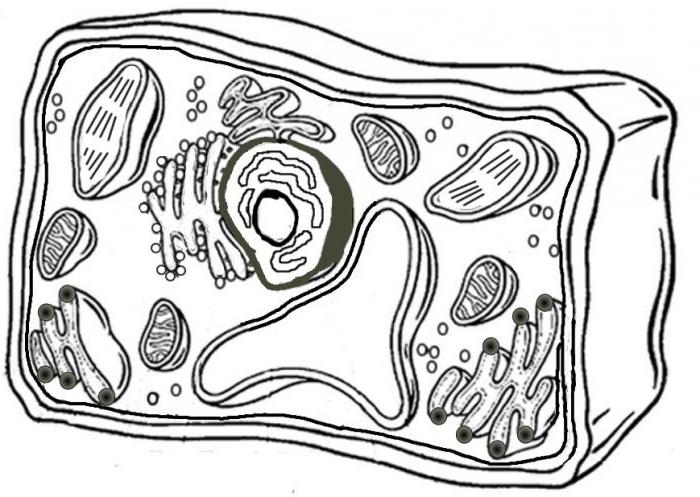
conclusions
So, we compared the plant and animal cells, their similarities and differences. Common are the plan of the structure, chemical processes and composition, division and genetic code. At the same time, plant and animal cells fundamentally differ in the way they nourish the organisms they form.
