Common human diseases caused by pathogenic fungi on the skin are called mycoses. The causative agents of mycoses belong to the class of dermatophytes, affect the upper and deep layers of the epidermis and are the cause of many diseases. Human skin serves as a source of nutrition for pathogenic dermatophyte fungi. Depending on the location of the spores and the structure of the hyphae, doctors diagnose fungal infections and choose treatment options for diseases.
Fungus can cause serious illness
Theoretical definition
Mushrooms are useful and harmful to humans. Fungal microorganisms live in the human body, creating a conditionally pathogenic environment. Under favorable conditions (for example, a decrease in immunity), the fungus can pose a threat, provoking various infectious diseases. All pathogenic fungi are classified into genera and species, families and classes with subclasses. According to the method of reproduction, pathogenic fungi make up eight classes, but only four are dangerous from a medical point of view:
- Ascomycetes. The most numerous class, including dermatophyte fungi, yeast-like and mold fungi.
- Zygomycetes (Mucor) - each genus of these fungi is pathogenic and dangerous to humans.
- Basidiomycetes. The causative agent of a serious disease, Cryptococcus neofarmans meningoencephalitis, is isolated separately.
- Deuteromycetes. These imperfect fungi (asexual reproduction) are the causative agents of skin mycoses.
In the etiology of skin fungal infectious diseases, yeast-like, as well as mold fungi and dermatophytes play the main role. The most common are fungi of the genus Trichophyton, Microsporum, Epidermophyton, Candida, Pityrosporum, Torulopsis, Exophiala werneckii, Piedraia hortae.
Dermatophytes are the causative agents of diseases of the skin, hair and nails. Medicine knows about fifty species of pathogenic fungi that can lead to the development of infectious diseases. Part of pathogenic fungi affects only the skin, the other part - the skin and subcutaneous tissue. Mycoses are caused by opportunistic fungi that are active in some immunodeficiency states of a person.
Morphology and reproduction
Pathogenic fungi have two main stages of formation and growth. During vegetative development, the thallus (the body of the fungus) is a kind of thallus of hyphae and budding cells. In the reproductive phase, reproduction occurs with the formation of cell units with similar characteristics. Mycelium form filamentous fibers of various shapes. The arrangement of cell units - sequentially one after another or in a chaotic manner.

Pathogenic fungi cause various diseases
The reproductive stage of development is characterized by sexual reproduction (perfect fungi) and asexual reproduction (imperfect fungi). Pathogenic microorganisms multiply in several ways:
- Division is possible due to the growth of the thallus and the formation of a mycelial filament with the formation of constrictions and the subsequent separation of young cells.
- Germination occurs by the formation of new sprouts on the mycelium. The protrusions reach the required size for the formation of a new mycelium.
- Budding. Part of the protoplasm and the nucleus of the mother cell form into a kidney, from which a new cell unit grows.
Due to the fact that the process of reproduction in an environment favorable for pathogenic fungi occurs quickly, infectious fungal diseases are characterized by the transience and progression of the disease in the absence of proper timely treatment. The mycelium spreads in the deep layers of the epidermis and it is impossible to prevent the further development of an infectious disease only by external influence.
The vital activity of pathogenic fungal microorganisms can proceed with symptoms and asymptomatically. Skin infections are characterized by the manifestation of signs of damage by pathogenic flora in the form of itching, changes in the color and structure of the skin, but not at the initial stage of the disease. That is, a person for a certain period of time may not suspect that pathogens of a fungal disease develop on the skin. The study of nail plates or skin flakes for pathogenic fungi is the first action when symptoms of infection with pathogenic pathogens appear.
Diseases of the skin, nails and hair
When in medicine they say that a fungal infection has affected human skin, this should be understood as the subsequent localization of pathogenic microorganisms on the hair and nails. With the growth of mycelium, the cells need more nutrition, and they begin to use as food not only particles of the surface and deep layers of the skin, but also the hairline and nail plates. Depending on the localization of pathogenic fungi on the skin and the type of pathogen, infectious diseases are classified into the following types:
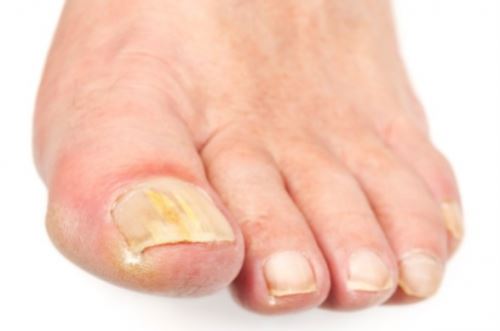
There are several options for classifying fungal infections - according to the etiology, clinical picture, nature and depth of skin lesions, different classifications of diseases are used in medical practice. The problem is that there is no single scheme according to which mycosis can be attributed to a specific category. So, according to different classifications, erythrasma is referred either to pseudomycosis or to keratomycosis. Although the causative agents of the disease are corynebacteria, and not a pathogenic fungus.
At the same time, actinomycosis is referred to as keratomycosis, but the causative agents of an infectious disease - pathogenic actinomycetes - are prokaryotes, they are closer to bacteria (coryne-, myco-, propionic) than to fungi. The complexity of the classification is exacerbated by the fact that after the identification of the causative agent of mycoses, they are divided according to the clinical picture, the localization of the mycelium and the stage of the disease.
The simplest and most understandable option is the division of infectious diseases into three large groups according to etiology:
- Mycoses caused by dermatophytes.
- Mycoses caused by yeast-like fungi.
- Mycosis, the causative agents of which are fungi.
The category of deep and systemic infectious diseases is distinguished separately. The pathogenicity of fungal microorganisms is dangerous for humans. A quarter of the world's population suffers from mycoses caused by various types of pathogenic fungi. The geography of the spread of pathogens is extensive, specific pathogens prevail for different continents. That is, in India, for example, you can quickly become infected with rhinosporidiosis, and in Central America - with coccidioidomycosis.
Symptoms, signs, causes of diseases
It is rather difficult to identify the causative agent of an infectious fungal disease at an early stage, since the mycelium only grows, there are few cell units in the colony, and they do not cause discomfort to a person during nutrition. When the number of pathogenic fungi reaches a huge number, external symptoms of mycoses appear:
- Feeling of discomfort, burning and itching.
- Change in normal skin color.
- Exfoliation of horny particles.
- Thinning hairline.
- Unpleasant odor, staining.
- Change in the structure of the nail plates.
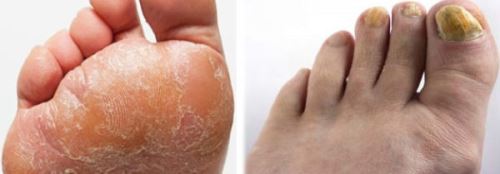
The occurrence of infection is manifested by certain symptoms
You can “get infected” with an infectious disease if you do not follow the rules of personal hygiene, contact with a sick person, wear someone else's shoes, visit public baths, swimming pools, changing rooms, use household items and hygiene of strangers. Against the background of reduced immunity, frequent use of antibiotics and glucocorticosteroids, HIV infection, an opportunistic fungus is rapidly developing. A favorable environment arises for its vital activity, “dormant” cells begin to actively multiply and form a branched fungal mycelium in the surface and deep layers of the epidermis, and a pronounced infiltrate, often of a granular structure, on the skin.
Diagnostic methods
To start treatment, it is necessary to accurately establish the etiology of the disease and the clinical picture. A visual inspection by a specialized specialist is not enough. It is mandatory to carry out laboratory diagnostics of sowing a pathogenic fungus. Since all types of microorganisms have a different pattern of mycelium formation and different localization on the skin, drugs should not slow down the growth of spores, but completely exterminate the colony. The following methods are used to diagnose mycoses:

Additionally, a luminescent study is carried out in case of damage to the hair by a pathogenic fungus. The reliability of diagnosis is especially high in the presence of microsporums in the hairline. Immunological and biological studies are used to identify the causes of infection. The main group of fungi pathogenic to humans are dermatophytes, so it is most often necessary to treat mycoses caused by these microorganisms.
Therapeutic therapy for mycoses
Infectious mycoses, which cause pathogenic fungal microorganisms, are contagious; upon contact with a sick person, healthy people become infected. But this does not require isolation of patients and the introduction of quarantine measures. The main task is to provide the patient with correct and timely treatment, create conditions under which the patient will carefully monitor personal hygiene, and avoid direct contact with other people - shaking hands, visiting public places with water procedures, changing rooms and showers. Antifungal drugs must meet the following requirements:
- good penetration into cells and tissues;
- broad or selective action;
- compatibility with other drugs;
- non-toxic, no resistance;
- stable results, availability.

Treatment of the fungus should be carried out with drugs prescribed by a doctor.
Treatment is prescribed only after laboratory tests. For each type of pathogenic fungi of the skin and mycosis of different parts of the body, different drugs are used. Carefully choose treatment during pregnancy - drugs should not harm the fetus. Treatment should be comprehensive - at the same time it is necessary to slow down the growth of a pathogenic fungus, restore the patient's immunity, destroy the pathogen, eliminate the factors that provoked the infectious disease. Treatment options:

In order not to have to resort to extreme measures, mycoses should be treated at the first sign of infection with a fungus. In many cases, patients mistakenly believe that problems on the skin, nails, soles of the feet or hair are caused by a lack of vitamins and nutrients in the body, physical factors or allergies. But if the fungus penetrates into the deep layers of the epidermis, it is not easy to destroy it, and the treatment will take a long time.
In order not to get infected, you need to carefully observe the rules of personal hygiene, maintain immunity. If a pathogenic fungus has settled in the body, you need to contact a specialist, hand over the material for laboratory and research, and strictly follow the recommendations of the attending physician.
